Recognition of pathogen-associated nucleic acids by endosomal nucleic acid-sensing toll-like receptors
- PMID: 23369718
- PMCID: PMC7109797
- DOI: 10.1093/abbs/gms122
Recognition of pathogen-associated nucleic acids by endosomal nucleic acid-sensing toll-like receptors
Abstract
Foreign nucleic acids, the essential signature molecules of invading pathogens that act as danger signals for host cells, are detected by endosomal nucleic acid-sensing toll-like receptors (TLRs) 3, 7, 8, 9, and 13. These TLRs have evolved to recognize 'non-self' nucleic acids within endosomal compartments and rapidly initiate innate immune responses to ensure host protection through induction of type I interferons, inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and co-stimulatory molecules and maturation of immune cells. In this review, we highlight our understanding of the recognition of pathogen-associated nucleic acids and activation of corresponding signaling pathways through endosomal nucleic acid-sensing TLRs 3, 7, 8, 9, and 13 for an enormous diversity of pathogens, with particular emphasis on their compartmentalization, intracellular trafficking, proteolytic cleavage, autophagy, and regulatory programs.
Figures
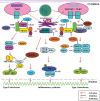
References
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity. 2011;34:637–650. - PubMed
-
- Barbalat R, Ewald SE, Mouchess ML, Barton GM. Nucleic acid recognition by the innate immune system. Ann Rev Immunol. 2011;29:185–214. - PubMed
-
- Hansena JD, Vojtechb LN, Laingc KJ. Sensing disease and danger: a survey of vertebrate PRRs and their origins. Dev Comp Immunol. 2011;35:886–897. - PubMed
-
- Kang JY, Lee JO. Structural biology of the toll-like receptor family. Annu Rev Biochem. 2011;80:917–941. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

