Global and regional burden of hospital admissions for severe acute lower respiratory infections in young children in 2010: a systematic analysis
- PMID: 23369797
- PMCID: PMC3986472
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61901-1
Global and regional burden of hospital admissions for severe acute lower respiratory infections in young children in 2010: a systematic analysis
Abstract
Background: The annual number of hospital admissions and in-hospital deaths due to severe acute lower respiratory infections (ALRI) in young children worldwide is unknown. We aimed to estimate the incidence of admissions and deaths for such infections in children younger than 5 years in 2010.
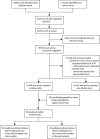
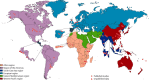
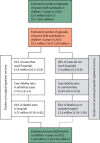
Methods: We estimated the incidence of admissions for severe and very severe ALRI in children younger than 5 years, stratified by age and region, with data from a systematic review of studies published between Jan 1, 1990, and March 31, 2012, and from 28 unpublished population-based studies. We applied these incidence estimates to population estimates for 2010, to calculate the global and regional burden in children admitted with severe ALRI in that year. We estimated in-hospital mortality due to severe and very severe ALRI by combining incidence estimates with case fatality ratios from hospital-based studies.
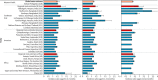
Findings: We identified 89 eligible studies and estimated that in 2010, 11·9 million (95% CI 10·3-13·9 million) episodes of severe and 3·0 million (2·1-4·2 million) episodes of very severe ALRI resulted in hospital admissions in young children worldwide. Incidence was higher in boys than in girls, the sex disparity being greatest in South Asian studies. On the basis of data from 37 hospital studies reporting case fatality ratios for severe ALRI, we estimated that roughly 265,000 (95% CI 160,000-450,000) in-hospital deaths took place in young children, with 99% of these deaths in developing countries. Therefore, the data suggest that although 62% of children with severe ALRI are treated in hospitals, 81% of deaths happen outside hospitals.
Interpretation: Severe ALRI is a substantial burden on health services worldwide and a major cause of hospital referral and admission in young children. Improved hospital access and reduced inequities, such as those related to sex and rural status, could substantially decrease mortality related to such infection. Community-based management of severe disease could be an important complementary strategy to reduce pneumonia mortality and health inequities.
Funding: WHO.
Copyright © 2013 World Health Organization. Published by Elsevier Ltd/Inc/BV. All rights reserved. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Acute lower respiratory infections in developing countries.Lancet. 2013 Apr 20;381(9875):1341-1342. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)62178-3. Epub 2013 Jan 29. Lancet. 2013. PMID: 23369798 No abstract available.
References
-
- Liu L, Johnson HL, Cousens S. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality: an updated systematic analysis for 2010 with time trends since 2000. Lancet. 2012;379:2151–2161. - PubMed
-
- Department of Child and Adolescent Health . Handbook: IMCI integrated management of childhood illness. World Health Organization; Geneva: 2005.
-
- Nair H, Brooks WA, Katz M. Global burden of respiratory infections due to seasonal influenza in young children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2011;378:1917–1930. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

