Circulating breast tumor cells exhibit dynamic changes in epithelial and mesenchymal composition
- PMID: 23372014
- PMCID: PMC3760262
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1228522
Circulating breast tumor cells exhibit dynamic changes in epithelial and mesenchymal composition
Erratum in
-
Erratum for the Report "Circulating Breast Tumor Cells Exhibit Dynamic Changes in Epithelial and Mesenchymal Composition" by M. Yu, A. Bardia, B. S. Wittner, S. L. Stott, M. E. Smas, D. T. Ting, S. J. Isakoff, J. C. Ciciliano, M. N. Wells, A. M. Shah, K. F. Concannon, M. C. Donaldson, L. V. Sequist, E. Brachtel, D. Sgroi, J. Baselga, S. Ramaswamy, M. Toner, D. A. Haber, S. Maheswaran.Science. 2019 Jan 25;363(6425):eaaw7579. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw7579. Science. 2019. PMID: 30679345 No abstract available.
Abstract
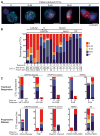
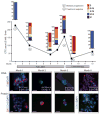
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of adherent epithelial cells to a migratory mesenchymal state has been implicated in tumor metastasis in preclinical models. To investigate its role in human cancer, we characterized EMT in circulating tumor cells (CTCs) from breast cancer patients. Rare primary tumor cells simultaneously expressed mesenchymal and epithelial markers, but mesenchymal cells were highly enriched in CTCs. Serial CTC monitoring in 11 patients suggested an association of mesenchymal CTCs with disease progression. In an index patient, reversible shifts between these cell fates accompanied each cycle of response to therapy and disease progression. Mesenchymal CTCs occurred as both single cells and multicellular clusters, expressing known EMT regulators, including transforming growth factor (TGF)-β pathway components and the FOXC1 transcription factor. These data support a role for EMT in the blood-borne dissemination of human breast cancer.
Figures


Comment in
-
Breast cancer: Circulating and dynamic EMT.Nat Rev Cancer. 2013 Mar;13(3):148. doi: 10.1038/nrc3475. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23407577 No abstract available.
-
Breast cancer: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in human breast cancer samples.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013 Apr;10(4):184. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2013.26. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23419957 No abstract available.
-
Tumor dissemination: an EMT affair.Cancer Cell. 2013 Mar 18;23(3):272-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.03.004. Cancer Cell. 2013. PMID: 23518345
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

