Systematic identification of signal-activated stochastic gene regulation
- PMID: 23372015
- PMCID: PMC3751578
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1231456
Systematic identification of signal-activated stochastic gene regulation
Abstract
Although much has been done to elucidate the biochemistry of signal transduction and gene regulatory pathways, it remains difficult to understand or predict quantitative responses. We integrate single-cell experiments with stochastic analyses, to identify predictive models of transcriptional dynamics for the osmotic stress response pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We generate models with varying complexity and use parameter estimation and cross-validation analyses to select the most predictive model. This model yields insight into several dynamical features, including multistep regulation and switchlike activation for several osmosensitive genes. Furthermore, the model correctly predicts the transcriptional dynamics of cells in response to different environmental and genetic perturbations. Because our approach is general, it should facilitate a predictive understanding for signal-activated transcription of other genes in other pathways or organisms.
Figures

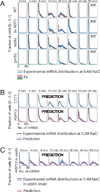

Similar articles
-
An Optogenetic Platform for Real-Time, Single-Cell Interrogation of Stochastic Transcriptional Regulation.Mol Cell. 2018 May 17;70(4):745-756.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.04.012. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29775585 Free PMC article.
-
Stochastic analysis of the GAL genetic switch in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: modeling and experiments reveal hierarchy in glucose repression.BMC Syst Biol. 2008 Nov 17;2:97. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-2-97. BMC Syst Biol. 2008. PMID: 19014615 Free PMC article.
-
Stochastic tuning of gene expression enables cellular adaptation in the absence of pre-existing regulatory circuitry.Elife. 2018 Apr 5;7:e31867. doi: 10.7554/eLife.31867. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29620524 Free PMC article.
-
The response to heat shock and oxidative stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2012 Apr;190(4):1157-95. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.128033. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22209905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The stress response in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae].Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 2004 Jan-Jun;46(1-2):24-46. Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 17061523 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
BAYESIAN INFERENCE OF STOCHASTIC REACTION NETWORKS USING MULTIFIDELITY SEQUENTIAL TEMPERED MARKOV CHAIN MONTE CARLO.Int J Uncertain Quantif. 2020;10(6):515-542. doi: 10.1615/int.j.uncertaintyquantification.2020033241. Int J Uncertain Quantif. 2020. PMID: 34007522 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental and engineering approaches to intracellular communication.Essays Biochem. 2018 Oct 26;62(4):515-524. doi: 10.1042/EBC20180024. Print 2018 Oct 26. Essays Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30139878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monte Carlo samplers for efficient network inference.PLoS Comput Biol. 2023 Jul 18;19(7):e1011256. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011256. eCollection 2023 Jul. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023. PMID: 37463156 Free PMC article.
-
Analytic approaches to stochastic gene expression in multicellular systems.Biophys J. 2013 Dec 17;105(12):2629-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.10.033. Biophys J. 2013. PMID: 24359735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using flow cytometry and multistage machine learning to discover label-free signatures of algal lipid accumulation.Phys Biol. 2019 Jul 22;16(5):055001. doi: 10.1088/1478-3975/ab2c60. Phys Biol. 2019. PMID: 31234155 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

