Safety and efficacy of donepezil hydrochloride in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease: Findings of an observational study
- PMID: 23372236
- PMCID: PMC3554965
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5545.104820
Safety and efficacy of donepezil hydrochloride in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease: Findings of an observational study
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD), a progressive brain disorder, is the most common cause of dementia among the elderly. Donepezil hydrochloride is a potent, reversible, and highly selective inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase (AChE). It is chemically distinct from other cholinesterase (ChE) inhibitors which are effective in the treatment of AD.
Objectives: To evaluate the safety and efficacy of donepezil hydrochloride therapy over a 12 weeks period in patients with mild to moderate AD in Indian population.
Materials and methods: In this post-marketing study, patients with mild to moderate AD received oral donepezil hydrochloride 5 mg/day for 4 weeks followed by 10 mg/day for 8 weeks. Patients were assessed 4 times weekly for cognition on 'Mini Mental Status Examination (MMSE) scale', and function on 'Activities of Daily Living (ADL) index'. Clinicians and caregivers assessment of safety and efficacy was assessed on a 5-point rating scale.
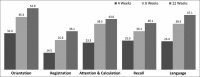
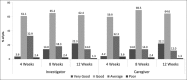
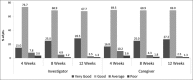
Results: One hundred and seventy two of one hundred and eighty two patients completed 12 weeks of study period. MMSE score significantly improved (P<0.0001) from 16.72 at baseline to 19.77 after 12 weeks, and there was significant improvement (P<0.05) in ADL index in 13 of 17 domains after 12 weeks. Caregivers and clinicians rated the therapy as very good to good in >80% and >90% patients, respectively. Adverse events were consistent with the known pharmacological and safety profile of donepezil.
Conclusions: Donepezil is well tolerated in Indian patients with mild to moderate AD with significant improvement in cognition and function.
Keywords: Alzheimer's; cognition; dementia; donepezil.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of donepezil, galantamine and rivastigmine in 938 Italian patients with Alzheimer's disease: a prospective, observational study.CNS Drugs. 2010 Feb;24(2):163-76. doi: 10.2165/11310960-000000000-00000. CNS Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20088621
-
Efficacy and safety of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease: results of a global, multinational, clinical experience study.Drugs Aging. 2004;21(1):43-53. doi: 10.2165/00002512-200421010-00004. Drugs Aging. 2004. PMID: 14715043
-
Perspectives in the management of Alzheimer's disease: clinical profile of donepezil.Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 1998;9 Suppl 3:29-42. doi: 10.1159/000051201. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 1998. PMID: 9853200 Review.
-
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the efficacy and safety of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease in the nursing home setting.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2001 Dec;49(12):1590-9. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2001. PMID: 11843990 Clinical Trial.
-
Donepezil: a review of its use in Alzheimer's disease.Drugs Aging. 2000 Mar;16(3):199-226. doi: 10.2165/00002512-200016030-00005. Drugs Aging. 2000. PMID: 10803860 Review.
Cited by
-
The Relieving Effects of BrainPower Advanced, a Dietary Supplement, in Older Adults with Subjective Memory Complaints: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:7898093. doi: 10.1155/2016/7898093. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 27190539 Free PMC article.
-
Plant-based flavonoids and their nanoparticles: Latest arsenal against Alzheimer's disease.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.1007/s13346-025-01906-9. Online ahead of print. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40587047 Review.
References
-
- Medez MF, Cummings JL. Dementia Significance, Definition and Epidemiology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Elseveir; 2006. Dementia: A Clinical Approach; pp. 1–12.
-
- Chung JA, Cummings JL. Neurobehavioral and neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer's disease: Characteristics and treatment. Neurol Clin. 2000;18:829–46. - PubMed
-
- Buckwalter K, Hall G. Alzheimer's disease. In: McBride AB, Austin JK, editors. Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing. Philadelphia Pa: WB Saunders Co; 1996. pp. 348–2.
-
- Cardozo MG, Iimura Y, Sugimoto H, Yamanishi Y, Hopfinger AJ. ‘QSAR anaylsis of the substituted indandone and benzylpiperidine rings of a series of indandone-benzylpiperidine inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. J Med Chem. 1992;35:584–9. - PubMed
-
- Cardozo MG, Kawai T, Iimura Y, Sugimoto H, Yamanishi Y, Hopfinger AJ. Conformational analysis and molecular shape comparisons of a series of indanone-benzylpiperidine inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. J Med Chem. 1992;35:590–601. - PubMed