(99m)Tc glucarate as a potential radiopharmaceutical agent for assessment of tumor viability: from bench to the bed side
- PMID: 23372437
- PMCID: PMC3555394
- DOI: 10.4103/1450-1147.103405
(99m)Tc glucarate as a potential radiopharmaceutical agent for assessment of tumor viability: from bench to the bed side
Abstract
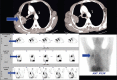
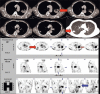
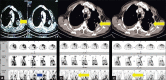
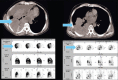
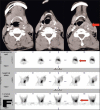
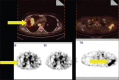
Several radiotracers have been used for assessing cell death, whether by necrosis or apoptosis. (99m)Tc glucarate, which has initially been reported to be concentrating/accumulating in myocardial infarction or zones of cerebral injury, has also shown some tumor-seeking properties in a few preliminary studies. Under International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)'s coordinated research program, we report here the standardization, quality control, and clinical evaluation (detection, evaluation of response, and comparison with (18)F Fluorodeoxyglucose) of this tracer in well-characterized lung cancer and head neck malignancies in a single-arm prospective observational study. Forty-seven patients (29 inoperable lung carcinoma and 18 head and neck malignancies) were prospectively enrolled and underwent (99m)Tc glucarate imaging [whole body planar and single-photon emission computed tomography of the region of interest] 4-5 hours after injection of 20 mCi of the radiopharmaceutical. Excellent (99m)Tc glucarate concentration was noted in the target lesion in lung cancer and head and neck malignancies. The sensitivity was found to be better in lung cancer. Avid concentration of tracer was seen in the metastatic sites. During response evaluation, the glucarate concentration correlated well with the clinical and other radiological findings. (99m)Tc glucarate showed avid concentration of tracer in the tumor, suggesting it to be a potential tumor imaging agent which can be used for detection and assessment of therapeutic response in malignancy.
Keywords: 99mTc glucarate; SPECT imaging; Tumor viability.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Imam SK. Molecular nuclear imaging: The radiopharmaceuticals (review) Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2005;20:163–72. - PubMed
-
- Fletcher JW, Djulbegovic B, Soares HP, Siegel BA, Lowe VJ, Lyman GH, et al. Recommendations on the use of 18F-FDG PET in oncology. J Nucl Med. 2008;49:480–508. - PubMed
-
- Ballinger JR, Proulx A, Ruddy TD. Stable kit formation of technetium- 99m-glucarate. Radiat Appl Instrum Part A. 1991;42:405–6.
-
- Yaoita H, Uehara T, Brownell AL, Rabito CA, Ahmad M, Khaw BA, et al. Localization of technetium-99m-glucarate in zones of acute cerebral injury. J Nucl Med. 1991;32:272–8. - PubMed
-
- Schimming R, Mason KA, Hunter N, Weil M, Kishi K, Milas L. Lack of correlation between mitotic arrest or apoptosis and antitumor effect of docetaxel. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1999;43:165–72. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

