(18)F-FLT-PET for Response Evaluation of MEK Inhibitor Selumetinib (AZD6244, ARRY-142886) in Patients with Solid Tumors
- PMID: 23372439
- PMCID: PMC3555396
- DOI: 10.4103/1450-1147.103413
(18)F-FLT-PET for Response Evaluation of MEK Inhibitor Selumetinib (AZD6244, ARRY-142886) in Patients with Solid Tumors
Abstract
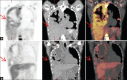
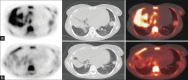
Selumetinib (AZD6244, ARRY-142886) is a potent, selective, uncompetitive inhibitor of MEK 1 / 2, part of the RAF/MEK/ERK protein kinase signal cascade, which is responsible for tumor. This pilot study was used to explore if (18)F-fluoro-l-thymidine (FLT), a thymidine analogue positron emission tomography (PET) tracer and a surrogate marker for proliferation, can be used as an early predictor of response for patients with solid cancers treated with Selumetinib. FLT-PET scans were performed in four patients at baseline and after 2 weeks of treatment with Selumetinib. FLT uptake in tumors was analyzed qualitatively and quantitatively by measuring standard uptake value (SUV) max in regions of interest (ROI). Results were compared to computed tomography (CT) scans (baseline and after 8 weeks), which were evaluated using the response evaluation criteria in solid tumors (RECIST) 1.0 criteria. One patient with melanoma showed both a qualitative and quantitative decrease in FLT uptake associated with a decrease in sum of longest diameter of 12% RECIST on CT evaluation. Another patient who had colorectal carcinoma (CRC) showed a significant increase in FLT uptake with initially stable, but eventually progressive disease on CT. The other two patients (one with melanoma and one with CRC) showed no significant changes in FLT uptake, whereas CT evaluation showed progressive disease. This is the first report describing changes in FLT-PET in patients receiving Selumetinib. In two patients, changes in FLT uptake as early as after 2 weeks of treatment were consistent with CT results after 8 weeks. Biomarkers to predict and evaluate treatment the outcome of targeted therapies are highly warranted. These initial results need further investigation.
Keywords: F-18 FLT; PET-CT; Selumetinib; treatment response.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
FLT-PET for early response evaluation of colorectal cancer patients with liver metastases: a prospective study.EJNMMI Res. 2017 Dec;7(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13550-017-0302-3. Epub 2017 Jul 10. EJNMMI Res. 2017. PMID: 28695424 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous positron emission tomography (PET) assessment of metabolism with ¹⁸F-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose (FDG), proliferation with ¹⁸F-fluoro-thymidine (FLT), and hypoxia with ¹⁸fluoro-misonidazole (F-miso) before and during radiotherapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): a pilot study.Radiother Oncol. 2011 Jan;98(1):109-16. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2010.10.011. Epub 2010 Nov 4. Radiother Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21056487
-
Imaging cellular proliferation during chemo-radiotherapy: a pilot study of serial 18F-FLT positron emission tomography/computed tomography imaging for non-small-cell lung cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009 Nov 15;75(4):1098-104. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.12.039. Epub 2009 Apr 20. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009. PMID: 19386444
-
Molecular PET and PET/CT imaging of tumour cell proliferation using F-18 fluoro-L-thymidine: a comprehensive evaluation.Nucl Med Commun. 2009 Dec;30(12):908-17. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0b013e32832ee93b. Nucl Med Commun. 2009. PMID: 19794320 Review.
-
Metabolic Imaging to Assess Treatment Response to Cytotoxic and Cytostatic Agents.Front Oncol. 2016 Jul 15;6:152. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2016.00152. eCollection 2016. Front Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27471678 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The enhanced in vivo activity of the combination of a MEK and a PI3K inhibitor correlates with [18F]-FLT PET in human colorectal cancer xenograft tumour-bearing mice.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 10;8(12):e81763. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081763. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24339963 Free PMC article.
-
3'-Deoxy-3'-18F-Fluorothymidine and 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography for the early prediction of response to Regorafenib in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer refractory to all standard therapies.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019 Jul;46(8):1713-1722. doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-04330-7. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31041456
-
Mechanisms shaping the role of ERK1/2 in cellular senescence (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2019 Feb;19(2):759-770. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9712. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 30535440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacodynamic Biomarker Development for PI3K Pathway Therapeutics.Transl Oncogenomics. 2016 Feb 21;7(Suppl 1):33-49. doi: 10.4137/TOG.S30529. eCollection 2015. Transl Oncogenomics. 2016. PMID: 26917948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FLT-PET for early response evaluation of colorectal cancer patients with liver metastases: a prospective study.EJNMMI Res. 2017 Dec;7(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13550-017-0302-3. Epub 2017 Jul 10. EJNMMI Res. 2017. PMID: 28695424 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banerji U, Camidge DR, Verheul HM, Agarwal R, Sarker D, Kaye SB, et al. The first-in-human study of the hydrogen sulfate (Hyd-sulfate) capsule of the MEK1 / 2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886): A phase I open-label multicenter trial in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:1613–23. - PubMed
-
- Bennouna J, Lang I, Valladares-Ayerbes M, Boer K, Adenis A, Escudero P, et al. A Phase II, open-label, randomised study to assess the efficacy and safety of the MEK1 / 2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) versus capecitabine monotherapy in patients with colorectal cancer who have failed one or two prior chemotherapeutic regimens. Invest New Drugs. 2011;29:1021–8. - PubMed
-
- Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:205–16. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

