Lipopolysaccharide induces IFN-γ production in human NK cells
- PMID: 23372571
- PMCID: PMC3556587
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00011
Lipopolysaccharide induces IFN-γ production in human NK cells
Abstract
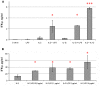
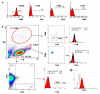
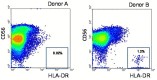
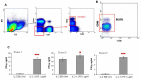
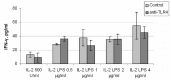
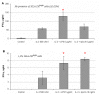
Natural killer (NK) cells have been shown to play a regulatory role in sepsis. According to the current view, NK cells become activated via macrophages or dendritic cells primed by lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Recently, TLR4 gene expression was detected in human NK cells suggesting the possibility of a direct action of LPS on NK cells. In this study, effects of LPS on NK cell cytokine production and cytotoxicity were studied using highly purified human NK cells. LPS was shown to induce IFN-γ production in the presence of IL-2 in NK cell populations containing>98% CD56(+) cells. Surprisingly, in the same experiments LPS decreased NK cell degranulation. No significant expression of markers related to blood dendritic cells, monocytes or T or B lymphocytes in the NK cell preparations was observed; the portions of HLA-DR(-bright), CD14(+), CD3(+), and CD20(+) cells amounted to less than 0.1% within the cell populations. No more than 0.2% of NK cells were shown to be slightly positive for surface TLR4 in our experimental system, although intracellular staining revealed moderate amounts of TLR4 inside the NK cell population. These cells were negative for surface CD14, the receptor participating in LPS recognition by TLR4. Incubation of NK cells with IL-2 or/and LPS did not lead to an increase in TLR4 surface expression. TLR4(-)CD56(+) NK cells isolated by cell sorting secreted IFN-γ in response to LPS. Antibody to TLR4 did not block the LPS-induced increase in IFN-γ production. We have also shown that R(e)-form of LPS lacking outer core oligosaccharide and O-antigen induces less cytokine production in NK cells than full-length LPS. We speculate that the polysaccharide fragments of LPS molecule may take part in LPS-induced IFN-γ production by NK cells. Collectively our data suggest the existence of a mechanism of LPS direct action on NK cells distinct from established TLR4-mediated signaling.
Keywords: NK cells; cytokine production; cytotoxicity; flow cytometry; lipopolysaccharide.
Figures
References
-
- Alter G., Malenfant J. M., Altfeld M. (2004). CD107a as a functional marker for the identification of natural killer cell activity. J. Immunol. Methods 294 15–22 - PubMed
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas K., Riley E. M. (2002). Innate immune response to malaria: rapid induction of IFN-gamma from human NK cells by live Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. J. Immunol. 169 2956–2963 - PubMed
-
- Becker I., Salaiza N., Aguirre M., Delgado J., Carrillo-Carrasco N., Kobeh L. G., et al. (2003). Leishmania lipophosphoglycan (LPG) activates NK cells through toll-like receptor-2. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 130 65–74 - PubMed
-
- Braun M., Müller B., ter Meer D., Raffegerst S., Simm B., Wilde S., Spranger S., et al. (2011). The CD6 scavenger receptor is differentially expressed on a CD56 natural killer cell subpopulation and contributes to natural killer-derived cytokine and chemokine secretion. J. Innate Immun. 3 420–434 - PubMed
-
- Chalifour A., Jeannin P., Gauchat J. F., Blaecke A., Malissard M., N’Guyen T., et al. (2004). Direct bacterial protein PAMP recognition by human NK cells involves TLRs and triggers α-defensin production. Blood 104 1778–1783 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

