Plunging ranula of the submandibular area
- PMID: 23372589
- PMCID: PMC3556294
Plunging ranula of the submandibular area
Abstract
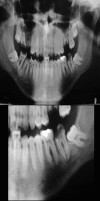
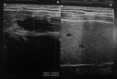
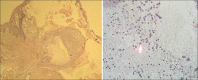
The term "ranula" is used to describe a diffuse swelling in the floor of the mouth caused by either a mucous extravasation or, less commonly, a mucous retention cyst derived from the major sublingual or submandibular salivary glands. The most common presentation of ranula is a painless, slow-growing, soft, and movable mass located in the floor of the mouth. Ranula may be simple or plunging. Simple ranula often present as masses in the floor of the mouth, limited to the mucous membranes. Diving ranulas extend through the facial plans, usually posterior to the mylohyoid muscle into the neck, and present as cervical masses. Thyroglossal duct cyst, branchial cleft cyst, cystic hygroma, submandibular sialadenitis, intramuscular hemangioma, cystic or neoplastic thyroid disease might be included in differential diagnosis. A variety of surgical procedures have been quoted in the literature ranging from marsupialization, excision of the ranula, sclerotherapy, and excision of the sublingual gland. The recurrence rate varies according to the procedure performed.
Keywords: Marsupialization; mouth floor; ranula; submandibular gland.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Plunging ranula.J Radiol Case Rep. 2011;5(6):18-24. doi: 10.3941/jrcr.v5i6.682. Epub 2011 Jun 1. J Radiol Case Rep. 2011. PMID: 22470797 Free PMC article.
-
Case report of the management of the ranula.J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019 Dec;45(6):357-363. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2019.45.6.357. Epub 2019 Dec 26. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019. PMID: 31966981 Free PMC article.
-
Plunging ranula with prestyloid parapharyngeal space, masticator space, and parotid gland extension.B-ENT. 2017;13(1 Suppl 27):57-60. B-ENT. 2017. PMID: 29557564
-
Surgical management of a large plunging ranula: A case report and review of diagnostic challenges.J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2025 Jun;126(3S):102219. doi: 10.1016/j.jormas.2025.102219. Epub 2025 Jan 3. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2025. PMID: 39756581 Review.
-
[Plunging ranula. Review].Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac Chir Orale. 2016 Apr;117(2):84-8. doi: 10.1016/j.revsto.2015.10.007. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac Chir Orale. 2016. PMID: 26809598 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Recurrent Plunging Ranula Due to a Sublingual Ectopic Gland: A Rare Clinical Entity.Cureus. 2024 Jan 19;16(1):e52590. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52590. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38371149 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Paediatric Oral Ranula: A Systematic Review.J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Sep;11(9):ZE06-ZE09. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/28498.10622. Epub 2017 Sep 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017. PMID: 29207849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrasound in the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of enoral and plunging ranula: a detailed and comparative analysis.J Ultrasound. 2023 Jun;26(2):487-495. doi: 10.1007/s40477-022-00743-7. Epub 2022 Dec 17. J Ultrasound. 2023. PMID: 36527568 Free PMC article.
-
Bluish swelling on the floor of the mouth.Malays Fam Physician. 2020 Mar 18;15(1):64-67. eCollection 2020. Malays Fam Physician. 2020. PMID: 32284810 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Peters E, Kola H, Doyle-Chan W. Bilateral congenital oral mucous extravasation cysts. Pediatr Dent. 1999;21:286–9. - PubMed
-
- Greenberg MS, Glick M, Ship JA. Burket oral medicine. 11th ed. Hamilton: Bcdecker; 2008. p. 203.
-
- El Beltagi AH, El Sayed Ahmed, Al Far, Al Sahmmary N. Horseshoe shaped, anterior crossing ranula, a case report. Eur J Radiol Extra. 2007;64:95–8.
-
- Wong KT, Lee YY, King AD, Ahuja AT. Imaging of cystic or cyst-like neck masses. Clin Radiol. 2008;63:613–22. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
