Avanafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction: initial data and clinical key properties
- PMID: 23372609
- PMCID: PMC3547533
- DOI: 10.1177/1756287212466282
Avanafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction: initial data and clinical key properties
Abstract
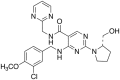
Orally active, selective inhibitors of phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE 5, cyclic GMP PDE), such as sildenafil, tadalafil and vardenafil, are currently the first-choice treatment options for the clinical management of erectile dysfunction (ED) of various etiologies and severities. However, a significant number of patients remain dissatisfied with the available therapies due a lack of efficacy or discomfort arising from adverse events. Several new PDE5 inhibitors, among which are avanafil (TA-1790), lodenafil, mirodenafil, udenafil, SLX-2101, JNJ-10280205 and JNJ-10287069, have recently been approved and introduced into the market or are in the final stages of their clinical development. Avanafil (marketed in the US under the brand name STENDRA(™)) has been developed by VIVUS Inc. (Mountain View, CA, USA) and has recently received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in the treatment of male ED. The drug has demonstrated improved selectivity for PDE5, is rapidly absorbed after oral administration with a fast onset of action and a plasma half-life that is comparable to sildenfil and vardenafil. In phase II and phase III clinical trials that included a large number of patients, avanafil has been shown to be effective and well tolerated. Owing to its favorable pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic profile, avanafil is considered as a promising new option in the treatment of ED. The present article summarizes the initial data and clinical key properties of avanafil.
Keywords: PDE5 inhibitors; avanafil; erectile dysfunction; oral pharmacotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Selectivity of avanafil, a PDE5 inhibitor for the treatment of erectile dysfunction: implications for clinical safety and improved tolerability.J Sex Med. 2012 Aug;9(8):2122-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2012.02822.x. Epub 2012 Jul 3. J Sex Med. 2012. PMID: 22759639
-
Mirodenafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction: a systematic review of the literature.World J Mens Health. 2014 Apr;32(1):18-27. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.2014.32.1.18. Epub 2014 Apr 25. World J Mens Health. 2014. PMID: 24872948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PDE5 inhibitors: are there differences?Can J Urol. 2006 Feb;13 Suppl 1:34-9. Can J Urol. 2006. PMID: 16526979 Review.
-
Avanafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. An updated review.Arch Esp Urol. 2014 Dec;67(10):839-47. Arch Esp Urol. 2014. PMID: 25582903 Review. English, Spanish.
-
Avanafil for erectile dysfunction.Ann Pharmacother. 2013 Oct;47(10):1312-20. doi: 10.1177/1060028013501989. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Ann Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 24259695 Review.
Cited by
-
Incorporating sodium deoxycholate endorsed the buccal administration of avanafil to heighten the bioavailability and duration of action.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2023 Sep;13(9):2297-2314. doi: 10.1007/s13346-023-01314-x. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 36853437
-
Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors: back and forward from cardiac indications.J Endocrinol Invest. 2016 Feb;39(2):143-51. doi: 10.1007/s40618-015-0340-5. Epub 2015 Jun 28. J Endocrinol Invest. 2016. PMID: 26122487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of benign prostatic hyperplasia: role of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors.Drugs Aging. 2014 Jun;31(6):425-39. doi: 10.1007/s40266-014-0177-1. Drugs Aging. 2014. PMID: 24811735 Review.
-
Role of interaction mode of phenanthrene derivatives as selective PDE5 inhibitors using molecular dynamics simulations and quantum chemical calculations.Mol Divers. 2025 Apr;29(2):1683-1696. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-10944-3. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 39080154
-
Avanafil for the Treatment of men With Erectile Dysfunction: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Am J Mens Health. 2019 Sep-Oct;13(5):1557988319880764. doi: 10.1177/1557988319880764. Am J Mens Health. 2019. PMID: 31672076 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allison M., Grant T., Obaidi M., Marenco T., Yee S., Day W. (2011) Pharmacokinetics of avanafil; a novel, rapidly-absorbed, selective PDE5 inhibitor for the treatment of mild to severe erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med 8(Suppl. 5): 466–467
-
- Aytac I., McKinlay J., Krane R. (1999) The likely worldwide increase in erectile dysfunction between 1995 and 2025 and some possible policy consequences. BJU Int 84: 50–56 - PubMed
-
- Belkoff L., McCullough A., Goldstein I., Di Donato K., Trask B., Bowden C. (2011) An open-label, long-term evaluation of the safety and tolerability of avanafil in men with erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med 8(Suppl. 5): 396 (abstract).
-
- Braun M., Wassmer G., Klotz T., Reifenrath B., Mathers M., Engelmann U. (2000) Epidemiology of erectile dysfunction: results of the Cologne Male Survey. Int J Impot Res (IJIR) 12: 305–311 - PubMed
-
- Eardley I., Donatucci C., Corbin J., El-Meliegy A., Hatzimouratidis K., McVary K., et al. (2010) Pharmacotherapy for erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med 7: 524–540 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

