Brain's alpha activity is highly reduced in euthymic bipolar disorder patients
- PMID: 23372616
- PMCID: PMC3253163
- DOI: 10.1007/s11571-011-9172-y
Brain's alpha activity is highly reduced in euthymic bipolar disorder patients
Abstract
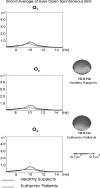
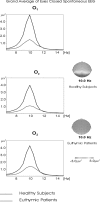
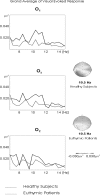
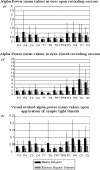
Brain's alpha activity and alpha responses belong to major electrical signals that are related to sensory/cognitive signal processing. The present study aims to analyze the spontaneous alpha activity and visual evoked alpha response in drug free euthymic bipolar patients. Eighteen DSM-IV euthymic bipolar patients (bipolar I n = 15, bipolar II n = 3) and 18 healthy controls were enrolled in the study. Patients needed to be euthymic at least for 4 weeks and psychotrop free for at least 2 weeks. Spontaneous EEG (4 min eyes closed, 4 min eyes open) and evoked alpha response upon application of simple visual stimuli were analyzed. EEG was recorded at 30 positions. The digital FFT-based power spectrum analysis was performed for spontaneous eyes closed and eyes open conditions and the response power spectrum was also analyzed for simple visual stimuli. In the analysis of spontaneous EEG, the ANOVA on alpha responses revealed significant results for groups (F(1,34) = 8.703; P < 0.007). Post-hoc comparisons showed that spontaneous EEG alpha power of healthy subjects was significantly higher than the spontaneous EEG alpha power of euthymic patients. Furthermore, visual evoked alpha power of healthy subjects was significantly higher than visual evoked alpha power of euthymic patients (F(1,34) = 4.981; P < 0.04). Decreased alpha activity in spontaneous EEG is an important pathological EEG finding in euthymic bipolar patients. Together with an evident decrease in evoked alpha responses, the findings may lead to a new pathway in search of biological correlates of cognitive impairment in bipolar disorder.
Keywords: Bipolar disorder; EEG alpha activity; Euthymia; Schizophrenia; Visual evoked alpha oscillations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decrease of theta response in euthymic bipolar patients during an oddball paradigm.Cogn Neurodyn. 2013 Jun;7(3):213-23. doi: 10.1007/s11571-012-9228-7. Epub 2012 Dec 9. Cogn Neurodyn. 2013. PMID: 24427202 Free PMC article.
-
Decrease of event-related delta oscillations in euthymic patients with bipolar disorder.Psychiatry Res. 2014 Jul 30;223(1):43-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2014.04.001. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Psychiatry Res. 2014. PMID: 24819306
-
Reduced long distance gamma (28-48 Hz) coherence in euthymic patients with bipolar disorder.J Affect Disord. 2011 Aug;132(3):325-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2011.02.028. Epub 2011 Apr 2. J Affect Disord. 2011. PMID: 21459454
-
Brain oscillations in bipolar disorder in search of new biomarkers.Suppl Clin Neurophysiol. 2013;62:207-21. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-7020-5307-8.00014-4. Suppl Clin Neurophysiol. 2013. PMID: 24053042 Review.
-
Brain oscillations as biomarkers in neuropsychiatric disorders: following an interactive panel discussion and synopsis.Suppl Clin Neurophysiol. 2013;62:343-63. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-7020-5307-8.00016-8. Suppl Clin Neurophysiol. 2013. PMID: 24053048 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurophysiological Hallmarks of Neurodegenerative Cognitive Decline: The Study of Brain Connectivity as A Biomarker of Early Dementia.J Pers Med. 2020 Apr 30;10(2):34. doi: 10.3390/jpm10020034. J Pers Med. 2020. PMID: 32365890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural oscillation in bipolar disorder: a systematic review of resting-state electroencephalography studies.Front Neurosci. 2024 Aug 21;18:1424666. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1424666. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39238928 Free PMC article.
-
Resting state EEG power and coherence abnormalities in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia.J Psychiatr Res. 2013 Dec;47(12):1893-901. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2013.09.009. Epub 2013 Sep 20. J Psychiatr Res. 2013. PMID: 24090715 Free PMC article.
-
Anxiety and depression: A top-down, bottom-up model of circuit function.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2023 Jul;1525(1):70-87. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14997. Epub 2023 May 2. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2023. PMID: 37129246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain oscillations in neuropsychiatric disease.Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2013 Sep;15(3):291-300. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2013.15.3/ebasar. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24174901 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aydemir Ö, Deveci A (2003) Validity and reliability of structured inter view for Hamilton depression rating scale seasonal affective disorders. Annual Spring Symposium of Psychiatric Association of abstract book, pp 187
-
- Babiloni C, Binetti G, Cassarino A, Dal Forno G, Del Percio C, Ferreri F, Ferri R, Frisoni G, Galderisi S, Hirata K, Lanuzza B, Miniussi C, Mucci A, Nobili F, Rodriguez G, Romani GL, Rossini PM. Sources of cortical rhythms in adults during physiological aging: a multi-centric EEG study. Human Brain Mapp. 2006;27:162–172. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20175. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Babiloni C, Cassetta E, Binetti G, Tombini M, Del Percio C, Ferreri F, Ferri R, Frisoni G, Lanuzza B, Nobili F, Parisi L, Rodriguez G, Frigerio L, Gurzì M, Prestia A, Vernieri F, Eusebi F, Rossini PM. Resting EEG sources correlate with attentional span in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Neurosci. 2007;25:3742–3757. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05601.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

