Activation of CD11b+ Kupffer cells/macrophages as a common cause for exacerbation of TNF/Fas-ligand-dependent hepatitis in hypercholesterolemic mice
- PMID: 23372642
- PMCID: PMC3553091
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049339
Activation of CD11b+ Kupffer cells/macrophages as a common cause for exacerbation of TNF/Fas-ligand-dependent hepatitis in hypercholesterolemic mice
Abstract
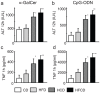
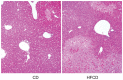
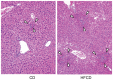
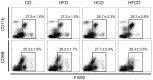
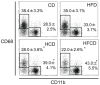
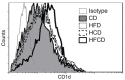
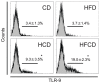
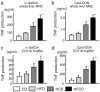
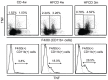
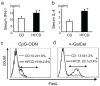
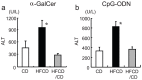
We have reported that the mouse hepatic injury induced by either α-galactosylceramide (α-GalCer) or bacterial DNA motifs (CpG-ODN) is mediated by the TNF/NKT cell/Fas-ligand (FasL) pathway. In addition, F4/80(+) Kupffer cells can be subclassified into CD68(+) subset with a phagocytosing capacity and CD11b(+) subset with a TNF-producing capacity. CD11b(+) subset increase if mice are fed high-fat and cholesterol diet (HFCD). The present study examined how a HFCD affects the function of NKT cells and F4/80(+) CD11b(+) subset and these hepatitis models. After the C57BL/6 mice received a HFCD, high-cholesterol diet (HCD), high-fat diet (HFD) and control diet (CD) for four weeks, the HFCD mice increased surface CD1d and intracellular TLR-9 expression by the CD11b(+) population compared to CD mice. Hepatic injury induced either by α-GalCer or CpG-ODN was more severe in HCD and HFCD mice compared to CD mice, which was in proportion to the serum TNF levels. In addition, liver cholesterol levels but not serum cholesterol levels nor liver triglyceride levels were involved in the aggravation of hepatitis. The FasL expression of NKT cells induced by both reagents was upregulated in HFCD mice. Furthermore, the liver mononuclear cells and purified F4/80(+) CD11b(+) subset from HFCD mice stimulated with either reagent in vitro produced a larger amount of TNF than did those from CD mice. Intracellular TNF production in F4/80(+) CD11b(+) cells was confirmed. The increased number of F4/80(+) CD11b(+) Kupffer cells/macrophages by HFCD and their enhanced TNF production thus play a pivotal role in TNF/NKT cell/FasL dependent hepatic injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Involvement of the TNF and FasL produced by CD11b Kupffer cells/macrophages in CCl4-induced acute hepatic injury.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 25;9(3):e92515. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092515. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24667392 Free PMC article.
-
The immunologic outcome of enhanced function of mouse liver lymphocytes and Kupffer cells by high-fat and high-cholesterol diet.Shock. 2011 Nov;36(5):484-93. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e31822dc6e4. Shock. 2011. PMID: 21937954
-
Alpha-galactosylceramide-induced liver injury in mice is mediated by TNF-alpha but independent of Kupffer cells.J Immunol. 2005 Aug 1;175(3):1540-50. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.3.1540. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16034092
-
Crosstalk of liver immune cells and cell death mechanisms in different murine models of liver injury and its clinical relevance.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2017 Jun;16(3):245-256. doi: 10.1016/s1499-3872(17)60014-6. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2017. PMID: 28603092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How to translate basic knowledge into clinical application of biologic therapy in spondyloarthritis.Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:369202. doi: 10.1155/2013/369202. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23840241 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Liver X Receptors Regulate Cholesterol Metabolism and Immunity in Hepatic Nonparenchymal Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 11;20(20):5045. doi: 10.3390/ijms20205045. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31614590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lowering the dietary omega-6: omega-3 does not hinder nonalcoholic fatty-liver disease development in a murine model.Nutr Res. 2015 May;35(5):449-59. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2015.04.003. Epub 2015 Apr 11. Nutr Res. 2015. PMID: 25934114 Free PMC article.
-
Activation and increase of radio-sensitive CD11b+ recruited Kupffer cells/macrophages in diet-induced steatohepatitis in FGF5 deficient mice.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 6;6:34466. doi: 10.1038/srep34466. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27708340 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages in the Aging Liver and Age-Related Liver Disease.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 30;9:2795. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02795. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30555477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of the TNF and FasL produced by CD11b Kupffer cells/macrophages in CCl4-induced acute hepatic injury.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 25;9(3):e92515. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092515. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24667392 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bouwens L, Baekeland M, De Zanger R, Wisse E (1986) Quantitation, tissue distribution and proliferation kinetics of Kupffer cells in normal rat liver. Hepatology 6: 718–722. - PubMed
-
- Seki S, Habu Y, Kawamura T, Takeda K, Dobashi H, et al. (2000) The liver as a crucial organ in the first line of host defense: the roles of Kupffer cells, natural killer (NK) cells and NK1.1 Ag+ T cells in T helper 1 immune responses. Immunol Rev 174: 35–46. - PubMed
-
- Doherty DG, O'Farrelly C (2000) Innate and adaptive lymphoid cells in the human liver. Immunol Rev 174: 5–20. - PubMed
-
- Nakagawa R, Nagafune I, Tazunoki Y, Ehara H, Tomura H, et al. (2001) Mechanisms of the antimetastatic effect in the liver and of the hepatocyte injury induced by alpha-galactosylceramide in mice. J Immunol 166: 6578–6584. - PubMed
-
- Inui T, Nakagawa R, Ohkura S, Habu Y, Koike Y, et al. (2002) Age-associated augmentation of the synthetic ligand- mediated function of mouse NK1.1 ag(+) T cells: their cytokine production and hepatotoxicity in vivo and in vitro. J Immunol 169: 6127–6132. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

