Imaging CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling in ovarian cancer therapy
- PMID: 23372646
- PMCID: PMC3553093
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051500
Imaging CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling in ovarian cancer therapy
Abstract
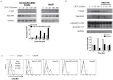
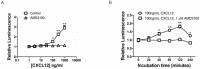
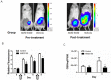
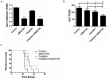
Chemokine CXCL12 and receptor CXCR4 have emerged as promising therapeutic targets for ovarian cancer, a disease that continues to have a dismal prognosis. CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling drives proliferation, survival, and invasion of ovarian cancer cells, leading to tumor growth and metastasis. Pleiotropic effects of CXCR4 in multiple key steps in ovarian cancer suggest that blocking this pathway will improve outcomes for patients with this disease. To quantify CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling in cell-based assays and living mouse models of ovarian cancer, we developed a click beetle red luciferase complementation reporter that detects activation of CXCR4 based on recruitment of the cytosolic adapter protein β-arrestin 2. Both in two-dimensional and three-dimensional cell cultures, we established that bioluminescence from this reporter measures CXCL12-dependent activation of CXCR4 and inhibition of this pathway with AMD3100, a clinically-approved small molecule that blocks CXCL12-CXCR4 binding. We used this imaging system to quantify CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling in a mouse model of metastatic ovarian cancer and showed that treatment with AMD3100 interrupted this pathway in vivo. Combination therapy with AMD3100 and cisplatin significantly decreased tumor burden in mice, although differences in overall survival were not significantly greater than treatment with either agent as monotherapy. These studies establish a molecular imaging reporter system for analyzing CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling in ovarian cancer, which can be used to investigate biology and therapeutic targeting of this pathway in cell-based assays and living mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Noninvasive imaging reveals inhibition of ovarian cancer by targeting CXCL12-CXCR4.Neoplasia. 2011 Dec;13(12):1152-61. doi: 10.1593/neo.111076. Neoplasia. 2011. PMID: 22241961 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CXCL12-CXCR4 axis in ovarian cancer metastasis and CXCL12-CXCR4 blockade with AMD3100 suppresses tumor cell migration and invasion in vitro.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Apr;234(4):3897-3909. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27163. Epub 2018 Sep 7. J Cell Physiol. 2019. Retraction in: J Cell Physiol. 2022 Mar;237(3):2005. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30517. PMID: 30191987 Retracted.
-
Imaging ligand-dependent activation of CXCR7.Neoplasia. 2009 Oct;11(10):1022-35. doi: 10.1593/neo.09724. Neoplasia. 2009. PMID: 19794961 Free PMC article.
-
The CXCL12 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 chemokine axis: Oncogenic properties, molecular targeting, and synthetic and natural product CXCR4 inhibitors for cancer therapy.Chin J Nat Med. 2018 Nov;16(11):801-810. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(18)30122-5. Chin J Nat Med. 2018. PMID: 30502762 Review.
-
The CXCL12-CXCR4/CXCR7 axis as a mechanism of immune resistance in gastrointestinal malignancies.Semin Cancer Biol. 2020 Oct;65:176-188. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.12.007. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020. PMID: 31874281 Review.
Cited by
-
CXCL5 expression in tumor tissues is associated with poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer.Oncol Lett. 2020 Nov;20(5):257. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12120. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32994820 Free PMC article.
-
High Expression of Stromal Cell-Derived Factor 1 (SDF-1) and NF-κB Predicts Poor Prognosis in Cervical Cancer.Med Sci Monit. 2017 Jan 11;23:151-157. doi: 10.12659/msm.899319. Med Sci Monit. 2017. PMID: 28074045 Free PMC article.
-
CXCL12-CXCR4 axis promotes the natural selection of breast cancer cell metastasis.Tumour Biol. 2014 Aug;35(8):7765-73. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-1816-1. Epub 2014 May 9. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 24810923 Free PMC article.
-
Translational research in oncology--10 years of progress and future prospects.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014 Nov;11(11):649-62. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2014.158. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25286976 Review.
-
Expression of CXCR4 in the Primary Lesion of Recurrent Metastatic Breast Cancer and Its Association With Prognosis.Int J Gen Med. 2025 Mar 18;18:1543-1553. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S511426. eCollection 2025. Int J Gen Med. 2025. PMID: 40123816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scotton C, Wilson J, Milliken D, Stamp G, Balkwill F (2001) Epithelial cancer cell migration: a role for chemokine receptors? Cancer Res 61: 3. - PubMed
-
- Foussat A, Balabanian K, Amara A, Bochet-Delbos L, Durand-Gasselin I, et al. (2001) Production of stromal cell-derived factor 1 by mesothelial cells and effects of this chemokine on peritoneal B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol 31: 350–359. - PubMed
-
- Jiang Y, Wu X, Shi B, Wu W, Yin G (2006) Expression of chemokine CXCL12 and its receptor CXCR4 in human epithelial ovarian cancer: an independent prognostic factor for tumor progression. Gynecol Oncol 103: 226–233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

