Mathematical modelling of polyamine metabolism in bloodstream-form Trypanosoma brucei: an application to drug target identification
- PMID: 23372667
- PMCID: PMC3553166
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053734
Mathematical modelling of polyamine metabolism in bloodstream-form Trypanosoma brucei: an application to drug target identification
Abstract
We present the first computational kinetic model of polyamine metabolism in bloodstream-form Trypanosoma brucei, the causative agent of human African trypanosomiasis. We systematically extracted the polyamine pathway from the complete metabolic network while still maintaining the predictive capability of the pathway. The kinetic model is constructed on the basis of information gleaned from the experimental biology literature and defined as a set of ordinary differential equations. We applied Michaelis-Menten kinetics featuring regulatory factors to describe enzymatic activities that are well defined. Uncharacterised enzyme kinetics were approximated and justified with available physiological properties of the system. Optimisation-based dynamic simulations were performed to train the model with experimental data and inconsistent predictions prompted an iterative procedure of model refinement. Good agreement between simulation results and measured data reported in various experimental conditions shows that the model has good applicability in spite of there being gaps in the required data. With this kinetic model, the relative importance of the individual pathway enzymes was assessed. We observed that, at low-to-moderate levels of inhibition, enzymes catalysing reactions of de novo AdoMet (MAT) and ornithine production (OrnPt) have more efficient inhibitory effect on total trypanothione content in comparison to other enzymes in the pathway. In our model, prozyme and TSHSyn (the production catalyst of total trypanothione) were also found to exhibit potent control on total trypanothione content but only when they were strongly inhibited. Different chemotherapeutic strategies against T. brucei were investigated using this model and interruption of polyamine synthesis via joint inhibition of MAT or OrnPt together with other polyamine enzymes was identified as an optimal therapeutic strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

 , total trypanothione;
, total trypanothione;  , exogenous methionine;
, exogenous methionine;  exogenous ornithine. Abbreviations of intra-cellular polyamine enzymes: MetPt, Met uptake enzyme; MAT, AdoMet synthase; AHS, methyltransferase; AdoMetDC, AdoMet decarboxylase; MetRcy, Met recycling enzyme; OrnPt, Orn uptake enzyme; ODC, Orn decarboxylase; SpdS, Spd synthase; TSHSyn,
exogenous ornithine. Abbreviations of intra-cellular polyamine enzymes: MetPt, Met uptake enzyme; MAT, AdoMet synthase; AHS, methyltransferase; AdoMetDC, AdoMet decarboxylase; MetRcy, Met recycling enzyme; OrnPt, Orn uptake enzyme; ODC, Orn decarboxylase; SpdS, Spd synthase; TSHSyn,  synthesis catalyst; TSHCpt,
synthesis catalyst; TSHCpt,  consumption catalyst.
consumption catalyst.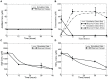

 equal to 0.0016, where the ODC activity was decreased by 90% within 24 hours of RNAi induction. Error bars are presented where appropriate data was available in the original papers.
equal to 0.0016, where the ODC activity was decreased by 90% within 24 hours of RNAi induction. Error bars are presented where appropriate data was available in the original papers.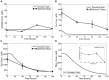
 equal to 0.0016. Error bars are presented where appropriate data was available in the original papers.
equal to 0.0016. Error bars are presented where appropriate data was available in the original papers.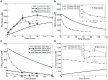
 ]) was modelled as a time-dependent variable with
]) was modelled as a time-dependent variable with  equal to 0.0004 to represent the 70% activity down-regulation within 2 days of induction; during knockout (KO) simulations, the factor
equal to 0.0004 to represent the 70% activity down-regulation within 2 days of induction; during knockout (KO) simulations, the factor  representing the percent of the complex AdoMetDC|prozyme taking up the total enzyme AdoMetDC is set to zero to represent full prozyme removal. In (D), MDL effects on Put and Spd dynamics were plotted. During the simulation, total enzyme concentration of AdoMetDC was modelled using a exponential decay function with
representing the percent of the complex AdoMetDC|prozyme taking up the total enzyme AdoMetDC is set to zero to represent full prozyme removal. In (D), MDL effects on Put and Spd dynamics were plotted. During the simulation, total enzyme concentration of AdoMetDC was modelled using a exponential decay function with  set to 0.07 to mimic a 98% knockdown within 1 hour of induction as specified experimentally. Error bars are presented where appropriate data was available in the original papers.
set to 0.07 to mimic a 98% knockdown within 1 hour of induction as specified experimentally. Error bars are presented where appropriate data was available in the original papers.
 set to 0.00045. Percentage changes of Put and
set to 0.00045. Percentage changes of Put and  at discrete time points over a simulated time span of 8 days were extracted from and normalised to the basal conditions of respective metabolites. For Put, only the percentage change at the end of the simulated time span was shown, since percentage changes for this metabolite over other time points were not reported in .
at discrete time points over a simulated time span of 8 days were extracted from and normalised to the basal conditions of respective metabolites. For Put, only the percentage change at the end of the simulated time span was shown, since percentage changes for this metabolite over other time points were not reported in .

 concentration values are calculated over a simulated time span of 5 days subject to a 90% decrease in individual enzyme velocities. A 90% knockdown of AdoMetDC enzyme concentration and a 90% prozyme knockdown were found to follow a similar pattern of
concentration values are calculated over a simulated time span of 5 days subject to a 90% decrease in individual enzyme velocities. A 90% knockdown of AdoMetDC enzyme concentration and a 90% prozyme knockdown were found to follow a similar pattern of  dynamics, and only prozyme inhibition is shown. In (B)
dynamics, and only prozyme inhibition is shown. In (B)  concentration values at the end of the simulated time span (5 days) are calculated subject to various degrees of knockdown (KD) for individual enzymes. In both figures, the percentage of
concentration values at the end of the simulated time span (5 days) are calculated subject to various degrees of knockdown (KD) for individual enzymes. In both figures, the percentage of  concentration under perturbed (
concentration under perturbed ( ) and normal (
) and normal ( ) conditions is plotted. In all cases, the maximum velocity of each enzyme is a time-dependent variable subject to specific inhibition within 24 hours of simulation.
) conditions is plotted. In all cases, the maximum velocity of each enzyme is a time-dependent variable subject to specific inhibition within 24 hours of simulation.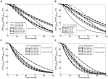
 concentration under perturbed (
concentration under perturbed ( , over a simulated time span of 5 days) and normal (
, over a simulated time span of 5 days) and normal ( ) conditions. In individual model simulations (A) and (B), a 10% enzyme knockdown (KD) of ODC and prozyme is applied in conjunction with down-regulation of other key pathway enzymes and the simulation results from individual and combined perturbations are compared. In (C) and (D), the inhibitory effects on
) conditions. In individual model simulations (A) and (B), a 10% enzyme knockdown (KD) of ODC and prozyme is applied in conjunction with down-regulation of other key pathway enzymes and the simulation results from individual and combined perturbations are compared. In (C) and (D), the inhibitory effects on  were examined for combinations of medium to strong depression of prozyme and TSHSyn, respectively, with different levels of knockdowns of other enzymes. In all cases, the maximum velocity of each enzyme is a time-dependent variable subject to specific inhibition within 24 hours.
were examined for combinations of medium to strong depression of prozyme and TSHSyn, respectively, with different levels of knockdowns of other enzymes. In all cases, the maximum velocity of each enzyme is a time-dependent variable subject to specific inhibition within 24 hours.Similar articles
-
Antitrypanosomal effects of polyamine biosynthesis inhibitors correlate with increases in Trypanosoma brucei brucei S-adenosyl-L-methionine.Biochem J. 1991 Mar 1;274 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):527-33. doi: 10.1042/bj2740527. Biochem J. 1991. PMID: 1672500 Free PMC article.
-
Regulated expression of an essential allosteric activator of polyamine biosynthesis in African trypanosomes.PLoS Pathog. 2008 Oct;4(10):e1000183. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000183. Epub 2008 Oct 24. PLoS Pathog. 2008. PMID: 18949025 Free PMC article.
-
Polyamine metabolism: a potential therapeutic target in trypanosomes.Science. 1980 Oct 17;210(4467):332-4. doi: 10.1126/science.6775372. Science. 1980. PMID: 6775372
-
Regulation and function of polyamines in African trypanosomes.Trends Parasitol. 2012 Feb;28(2):66-72. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2011.11.001. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Trends Parasitol. 2012. PMID: 22192816 Review.
-
Effects of antagonists of polyamine metabolism on African trypanosomes.Acta Trop. 1993 Sep;54(3-4):225-36. doi: 10.1016/0001-706x(93)90095-s. Acta Trop. 1993. PMID: 7902660 Review.
Cited by
-
The silicon trypanosome: a test case of iterative model extension in systems biology.Adv Microb Physiol. 2014;64:115-43. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800143-1.00003-8. Adv Microb Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24797926 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Muller S, Liebau E, Walter RD, Krauth-Siegel RL (2003) Thiol-based redox metabolism of protozoan parasites. Trends in Parasitology 19: 320–327. - PubMed
-
- Turrens JF (2004) Oxidative stress and antioxidant defence: a target for the treatment of diseases caused by parasitic protozoa. Molecular Aspects of Medicine 25: 211–220. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez-Caso C, Montanez R, Cascante M, Sanchez-Jimenez F, Medina MA (2006) Mathematical modelling of polyamine metabolism in mammals. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 281: 21799–21812. - PubMed
-
- Heby O, Persson L, Rentala M (2007) Targeting the polyamine biosynthetic enzymes: a promising approach to therapy of African sleeping sickness, chagas' disease and Leishmaniasis. Amino Acids 33: 359–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

