Sphingosine 1-phosphate mediates hyperalgesia via a neutrophil-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 23372844
- PMCID: PMC3555820
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055255
Sphingosine 1-phosphate mediates hyperalgesia via a neutrophil-dependent mechanism
Abstract
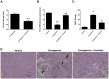
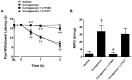
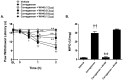
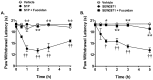
Novel classes of pain-relieving molecules are needed to fill the void between non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents and narcotics. We have recently shown that intraplantar administration of sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) in rats causes peripheral sensitization and hyperalgesia through the S1P(1) receptor subtype (S1PR(1)): the mechanism(s) involved are largely unknown and were thus explored in the present study. Intraplantar injection of carrageenan in rats led to a time-dependent development of thermal hyperalgesia that was associated with pronounced edema and infiltration of neutrophils in paw tissues. Inhibition of 1) S1P formation with SK-I, a sphingosine kinase inhibitor, 2) S1P bioavailability with the S1P blocking antibody Sphingomab, LT1002 (but not its negative control, LT1017) or 3) S1P actions through S1PR(1) with the selective S1PR(1) antagonist, W146 (but not its inactive enantiomer, W140) blocked thermal hyperalgesia and infiltration of neutrophils. Taken together, these findings identify S1P as an important contributor to inflammatory pain acting through S1PR(1) to elicit hyperalgesia in a neutrophil-dependant manner. In addition and in further support, we demonstrate that the development of thermal hyperalgesia following intraplantar injection of S1P or SEW2871 (an S1PR(1) agonist) was also associated with neutrophilic infiltration in paw tissues as these events were attenuated by fucoidan, an inhibitor of neutrophilic infiltration. Importantly, FTY720, an FDA-approved S1P receptor modulator known to block S1P-S1PR(1) signaling, attenuated carrageenan-induced thermal hyperalgesia and associated neutrophil infiltration. Targeting the S1P/S1PR(1) axis opens a therapeutic strategy for the development of novel non-narcotic anti-hyperalgesic agents.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- National CfHS (2006) Health, United States, 2006 Chartbook on Trends in the Health of Americans. Hyattsville, MD.
-
- Warner TD, Mitchell JA (2004) Cyclooxygenases: new forms, new inhibitors, and lessons from the clinic. FASEB J 18: 790–804. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

