Early referral to a nephrologist improved patient survival: prospective cohort study for end-stage renal disease in Korea
- PMID: 23372849
- PMCID: PMC3555934
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055323
Early referral to a nephrologist improved patient survival: prospective cohort study for end-stage renal disease in Korea
Abstract
The timing of referral to a nephrologist may influence the outcome of chronic kidney disease patients, but its impact has not been evaluated thoroughly. The results of a recent study showing an association between early referral and patient survival are still being debated. A total of 1028 patients newly diagnosed as end-stage renal disease (ESRD) from July 2008 to October 2011 were enrolled. Early referral (ER) was defined as patients meeting with a nephrologist more than a year before dialysis and dialysis education were provided, and all others were considered late referral (LR). The relationship of referral pattern with mortality in ESRD patients was explored using a Cox proportional hazards regression models. Time from referral to dialysis was significantly longer in 599 ER patients than in 429 LR patients (62.3 ± 58.9 versus 2.9 ± 3.4 months, P<0.001). Emergency HD using a temporary vascular catheter was required in 485 (47.2%) out of all patients and in 262 (43.7%) of ER compared with 223 (52.0%) of LR (P = 0.009). After 2 years of follow-up, the survival rate in ER was better than that in LR (hazard ratio [HR] 2.38, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.27-4.45, P = 0.007). In patients with diabetes nephropathy, patient survival was also significantly higher in ER than in LR (HR 4.74, 95% CI 1.73-13.00, P = 0.002). With increasing age, HR also increased. Timely referral to a nephrologist in the predialytic stage is associated with reduced mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
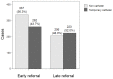
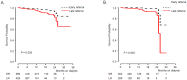

References
-
- NHIC (2004) 2003 National Health Insurance Statistical Yearbook. Seoul, Korea. National Health Insurance Corporation (NHIC).
-
- Jones C, Roderick P, Harris S, Rogerson M (2006) Decline in kidney function before and after nephrology referral and the effect on survival in moderate to advanced chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21: 2133–2143. - PubMed
-
- Stack AG (2002) Determinants of modality selection among incident US dialysis patients: results from a national study. J Am Soc Nephrol 13: 1279–1287. - PubMed
-
- Winkelmayer WC, Glynn RJ, Levin R, Owen W Jr, Avorn J (2001) Late referral and modality choice in end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int 60: 1547–1554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

