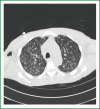
Acute respiratory distress syndrome with miliary tuberculosis: a fatal combination
- PMID: 23372959
- PMCID: PMC3547991
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2012.07.02
Acute respiratory distress syndrome with miliary tuberculosis: a fatal combination
Keywords: Miliary tuberculosis; acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictors and outcome of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by miliary tuberculosis: a retrospective study in Chongqing, China.BMC Infect Dis. 2012 May 20;12:121. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-12-121. BMC Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22607610 Free PMC article.
-
Miliary tuberculosis leading to acute respiratory distress syndrome: Clinical experience in pediatric intensive care.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2019 Dec;54(12):2003-2010. doi: 10.1002/ppul.24510. Epub 2019 Sep 9. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2019. PMID: 31496114
-
[Miliary tuberculosis associated with acute respiratory distress and pancytopenia in HIV-negative patient].Rev Clin Esp. 2001 Mar;201(3):130-3. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2565(01)70766-7. Rev Clin Esp. 2001. PMID: 11387821 Review. Spanish.
-
Miliary tuberculosis and adult respiratory distress syndrome.Intensive Care Med. 1987;13(3):175-82. doi: 10.1007/BF00254701. Intensive Care Med. 1987. PMID: 3584648
-
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in miliary tuberculosis: a twelve year experience.Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 1996 Jul-Sep;38(3):157-62. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 1996. PMID: 8987289 Review.
Cited by
-
Corticosteroid-induced exacerbation of cryptic miliary tuberculosis to acute respiratory distress syndrome: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Nov 13;99(46):e23204. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023204. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33181702 Free PMC article.
-
Miliary Tuberculosis Presenting with Hyponatremia and ARDS in an 82-Year-Old Immunocompetent Female.Pathogens. 2018 Sep 5;7(3):72. doi: 10.3390/pathogens7030072. Pathogens. 2018. PMID: 30189694 Free PMC article.
-
Miliary Tuberculosis in a Young Woman with Hemophagocytic Syndrome: A Case Report and Literature Review.Intern Med. 2017;56(12):1591-1596. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.56.8025. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28626190 Free PMC article.
-
Fatal Disseminated Tuberculous Peritonitis following Spontaneous Abortion: A Case Report.Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2014;2014:125609. doi: 10.1155/2014/125609. Epub 2014 Mar 4. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2014. PMID: 24716027 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharma SK, Mohan A, Sharma A, et al. Miliary tuberculosis: new insights into an old disease. Lancet Infect Dis 2005;5:415-30 - PubMed
-
- Piqueras AR, Marruecos L, Artigas A, et al. Miliary tuberculosis and adult respiratory distress syndrome. Intensive Care Med 1987;13:175-82 - PubMed
-
- Mohan A, Sharma SK, Pande JN. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in miliary tuberculosis: a twelve year experience. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci 1996;38:157-62 - PubMed
-
- Chapman CB, WHORTON CM. Acute generalized miliary tuberculosis in adults. N Engl J Med 1946;235:239-48 - PubMed
-
- Stead WW. Pathogenesis of tuberculosis: clinical and epidemiologic perspective. Rev Infect Dis 1989;11:S366-8 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources