Benefits of early aneurysm surgery: Southern Iran experience
- PMID: 23372972
- PMCID: PMC3551498
- DOI: 10.4103/2152-7806.105095
Benefits of early aneurysm surgery: Southern Iran experience
Abstract
Background: Neurovascular surgery has been practiced in Shiraz, the main referral center of the Southern Iran, for over 30 years; however, the trend has accelerated tremendously in recent years following subspecialization of neurovascular surgery in Shiraz, Department of Neurosurgery. Over 100 patients are operated each year, and nearly all are addressed during the first 72 hours after presentation.
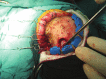
Methods: In this paper, we focus on the description of techniques we apply for early clipping of ruptured intracranial aneurysms in the anterior circulation. Improvements in outcome, mortality, and rebleeding rates are also discussed.
Results: Mortality and rebleeding rates have declined significantly since the institution of new techniques.
Conclusion: The establishment of early surgery for ruptured anterior circulation aneurysms through the lateral supraorbital approach along with specific anesthetic protocol has resulted in significant improvement of morbidity, mortality, and rebleeding rates at our department.
Keywords: Anterior circulation; early surgery; ruptured aneurysm; techniques.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Coil embolization for intracranial aneurysms: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(1):1-114. Epub 2006 Jan 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074479 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical Outcome of Patients with Very Small Intracranial Aneurysms: A Single-Center Experience from Southern Iran.World Neurosurg. 2017 Feb;98:470-478. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2016.11.086. Epub 2016 Nov 24. World Neurosurg. 2017. PMID: 27890758
-
Risk Factor Analysis for Poor Outcomes in Supraorbital Keyhole Aneurysm Clipping for Ruptured Anterior Circulation Aneurysms.World Neurosurg. 2018 Mar;111:e386-e394. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2017.12.071. Epub 2017 Dec 20. World Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 29274447
-
Lateral Supraorbital Approach for the Surgical Clipping of Ruptured Tiny Anterior Circulation Aneurysms.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2020 May;30(5):523-526. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2020.05.523. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2020. PMID: 32580852
-
Acutely Ruptured Intracranial Aneurysms Treated with Flow-Diverter Stents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018 Sep;39(9):1669-1675. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A5730. Epub 2018 Jul 26. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018. PMID: 30049721 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage (aSAH): Five consecutive years' experience of Fars province, Iran.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 30;12(11):e0189005. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189005. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29190810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alibai EA, Khani M. Incidence of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage and analysis of factors involved in early aneurysm rebleeding. Neurosurg Q. 2010;20:82–9.
-
- Allcock JM, Drake CG. Ruptured intracranial aneurysms-the role of arterial spasm. J Neurosurg. 1965;22:21–9. - PubMed
-
- Dalbayrak S, Altas M, Arslan R. The effects of timing of aneurysm surgery on vasospasm and mortality in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurol Belg. 2011;111:317–20. - PubMed
-
- Dashti R, Laakso A, Niemela M, Porras M, Celik O, Navratil O, et al. Application of microscope integrated indocyanine green video-angiography during microneurosurgical treatment of intracranial aneurysms: A review. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2010;107:107–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

