MicroRNA-100 regulates IGF1-receptor expression in metastatic pancreatic cancer cells
- PMID: 23373509
- PMCID: PMC4170730
- DOI: 10.3109/10520295.2012.762460
MicroRNA-100 regulates IGF1-receptor expression in metastatic pancreatic cancer cells
Abstract
Patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma have the lowest 5 year survival rate and yearly rates of incidence are nearly equal to the mortality rates. Long term cure rates by standard therapies are disappointing owing to disseminated disease at diagnosis and chemotherapeutic resistance. New therapeutic targets are necessary to decrease the progression of pancreatic cancer and the ability to identify targets specific to metastasis would improve patient care. We evaluated the levels of microRNA of metastatic and non-metastatic cell lines. The expression levels of microRNAs and mRNAs were determined using microarray analysis to examine and compare five pancreatic cancer cell lines, two that can metastasize in vivo (S2VP10 and S2CP9) and three that do not metastasize (MiaPaCa2, Panc-1 and ASPC-1). MicroRNA analysis indicated an increase in miR-100 and a decrease in miR-138 expression in metastatic cancer cells. Microarray analysis of different expressions of mRNAs in metastatic and non-metastatic pancreatic cell lines also indicated significantly increased insulin growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1-R) expression in metastatic pancreatic cancer cell lines compared to non-metastatic pancreatic cancer cell lines. To confirm microarray analysis results, western blot and immunocytochemistry were performed. Western blot revealed that IGF1-R expression exhibited in metastatic cancer cell lines a seven-fold increase compared to non-metastatic cell lines. In addition, downstream expressions of the proteins, GRB2 and phosphorylated PI3K, also were increased in aggressive cancer cell lines. Immunocytochemistry confirmed the linkage of IGF1-R to miR-100, because cells transfected with miR-100 inhibitor showed a decrease in IGF1-R. Cells transfected with a miR-138 mimic, however, did not affect IGF1-R expression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
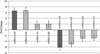

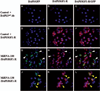
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-140 regulates cell growth and invasion in pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma by targeting iASPP.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2016 Feb;48(2):174-81. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmv127. Epub 2016 Jan 18. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2016. PMID: 26787707
-
Retinoic acid receptor antagonists inhibit miR-10a expression and block metastatic behavior of pancreatic cancer.Gastroenterology. 2009 Dec;137(6):2136-45.e1-7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.08.065. Epub 2009 Sep 10. Gastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 19747919
-
Involvement of CD40 targeting miR-224 and miR-486 on the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas.Ann Surg Oncol. 2009 Aug;16(8):2339-50. doi: 10.1245/s10434-009-0531-4. Epub 2009 May 28. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19475450
-
[Potential role of ezrin and its related microRNA in ovarian cancer invasion and metastasis].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2010 Oct;45(10):787-92. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 21176563 Chinese.
-
miRNAs in insulin resistance and diabetes-associated pancreatic cancer: the 'minute and miracle' molecule moving as a monitor in the 'genomic galaxy'.Curr Drug Targets. 2013 Sep;14(10):1110-7. doi: 10.2174/13894501113149990182. Curr Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 23834149 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of miR-100 expression with clinicopathological features and prognosis of patients with lung cancer.Oncol Lett. 2019 Aug;18(2):1318-1322. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10393. Epub 2019 May 22. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31423192 Free PMC article.
-
miR-100 Inhibits Cell Growth and Proliferation by Targeting HOXA1 in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Jan 20;13:593-602. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S228783. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32021301 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs that affect prostate cancer: emphasis on prostate cancer in African Americans.Biotech Histochem. 2013 Oct;88(7):410-24. doi: 10.3109/10520295.2013.807069. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Biotech Histochem. 2013. PMID: 23901944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in pancreatic cancer drug resistance: mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jan 15;12:1499111. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1499111. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 39882259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WISP1 induces ovarian cancer via the IGF1/αvβ3/Wnt axis.J Ovarian Res. 2022 Aug 13;15(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s13048-022-01016-x. J Ovarian Res. 2022. PMID: 35964060 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baserga R, Peruzzi F, Reiss K. The IGF-1 receptor in cancer biology. Int. J. Cancer. 2003a;107:873–877. - PubMed
-
- Baserga R, Prisco M, Yuan T. IGF-1 Receptor Signaling in Health and Disease. Georgetown, TX: Landes Bioscience; 2003b. pp. 120–140.
-
- Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, Aharonov R, Gilad S, Barad O, Barzilai A, Einat P, Einav U, Meiri E, Sharon E, Spector Y, Bentwich Z. Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat. Genet. 2005;37:766–770. - PubMed
-
- Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2006;6:857–866. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
