Fluorochrome-functionalized nanoparticles for imaging DNA in biological systems
- PMID: 23373524
- PMCID: PMC3800685
- DOI: 10.1021/nn305962n
Fluorochrome-functionalized nanoparticles for imaging DNA in biological systems
Abstract
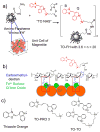
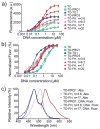
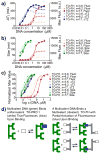
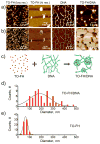
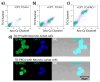
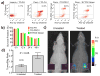
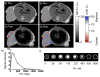
Attaching DNA binding fluorochromes to nanoparticles (NPs) provides a way of obtaining NPs that bind to DNA through fluorochrome mediated interactions. To obtain a nanoparticle (NP) that bound to the DNA in biological systems, we attached the DNA binding fluorochrome, TO-PRO 1 (TO), to the surface of the Feraheme (FH) NP, to obtain a fluorochrome-functionalized NP denoted TO-FH. When reacted with DNA in vitro, TO-FH formed microaggregates that were characterized by fluorescence, light scattering, and T2 changes. The formation of DNA/TO-FH microaggregates was also characterized by AFM, with microaggregates exhibiting a median size of 200 nm, and consisting of DNA and multiple TO-FH NPs whose individual diameters were only 25-35 nm. TO-FH failed to bind normal cells in culture, but treatment with chemotherapeutic agents or detergents yielded necrotic cells that bound TO-FH and vital fluorochromes similarly. The uptake of TO-FH by HT-29 xenografts (treated with 5-FU and oxaliplatin) was evident by surface fluorescence and MRI. Attaching multiple DNA binding fluorochromes to magnetic nanoparticles provides a way of generating DNA binding NPs that can be used to detect DNA detection by microaggregate formation in vitro, for imaging the DNA of necrotic cells in culture, and for imaging the DNA of a tumor treated with a chemotherapeutic agent. Fluorochrome functionalized NPs are a multimodal (magnetic and fluorescent), highly multivalent (n ≈ 10 fluorochromes/NP) nanomaterials useful for imaging the DNA of biological systems.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Marko MA, Chipperfield R, Birnboim HC. A Procedure for the Large-Scale Isolation of Highly Purified Plasmid DNA Using Alkaline Extraction and Binding to Glass Powder. Anal Biochem. 1982;121:382–387. - PubMed
-
- Rosi NL, Giljohann DA, Thaxton CS, Lytton-Jean AK, Han MS, Mirkin CA. Oligonucleotide-Modified Gold Nanoparticles for Intracellular Gene Regulation. Science. 2006;312:1027–1030. - PubMed
-
- Josephson L, Perez JM, Weissleder RW. Magnetic Nanosensors for the Detection of Oligonucleotide Sequences. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2001;40:3204–3206. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

