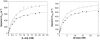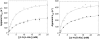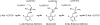Heavy-enzyme kinetic isotope effects on proton transfer in alanine racemase
- PMID: 23373756
- PMCID: PMC3579662
- DOI: 10.1021/ja3101243
Heavy-enzyme kinetic isotope effects on proton transfer in alanine racemase
Abstract
The catalytic effects of perdeuterating the pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzyme alanine racemase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus are reported. The mass of the heavy perdeuterated form is ~5.5% greater than that of the protiated form, causing kinetic isotope effects (KIEs) of ~1.3 on k(cat) and k(cat)/K(M) for both L- and D-alanine. These values increase when Cα-deuterated alanine is used as the substrate. The heavy-enzyme KIEs of ~3 on k(cat)/K(M) with deuterated substrates are greater than the product of the individual heavy-enzyme and primary substrate KIEs. This breakdown of the rule of the geometric mean is likely due to coupled motion between the protein and the proton-transfer reaction coordinate in the rate-limiting step. These data implicate a direct role for protein vibrational motions in barrier crossing for proton-transfer steps in alanine racemase.
Figures
References
-
- Klinman JP. Nat Chem. 2010;2:907. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous