In vivo calibration of microdialysis using infusion of stable-isotope labeled neurotransmitters
- PMID: 23374073
- PMCID: PMC3656751
- DOI: 10.1021/cn300199m
In vivo calibration of microdialysis using infusion of stable-isotope labeled neurotransmitters
Abstract
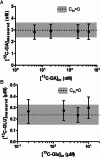
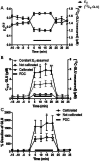
In vivo calibration of microdialysis probes is required for interpreting measured concentrations. The most popular method of in vivo calibration is no-net-flux (NNF), which requires infusing several concentrations of neurotransmitters to determine in vivo recoveries (extraction fraction or Ed) and extracellular concentrations. A new method for in vivo calibration of microdialysis of neurotransmitters using glutamate (GLU) and dopamine (DA) as model analytes is reported. (13)C6-DA and (13)C5-GLU were perfused through microdialysis probes as internal calibrators. Using liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry, it was possible to distinguish the (13)C-forms from the endogenous forms of each neurotransmitter. Ed was directly calculated by measuring the loss of the (13)C-forms during infusion. The measured endogenous (12)C forms of the neurotransmitters could be corrected for Ed to give calibrated extracellular concentrations in vivo. Retrodialysis of stable-isotope-labeled (SIL) neurotransmitters gave Ed and extracellular concentrations of (13)C5-GLU and (13)C6-DA that matched no-net-flux measurements; however, the values were obtained in a fraction of time because no added measurements were required to obtain the calibration. Ed was reduced during uptake inhibition for GLU and DA when measured by SIL retrodialysis. Because Ed is directly measured at each microdialysis fraction, it was possible to monitor changes in Ed under transient conditions created by systemic injection of uptake inhibitors. The results show that DA and GLU concentrations are underestimated by as much as 50% if not corrected for Ed during uptake inhibition. SIL retrodialysis provides equivalent information to NNF at much reduced time and animal use.
Figures




References
-
- Chefer V. I.; Zapata A.; Shippenberg T. S.; Bungay P. M. (2006) Quantitative no-net-flux microdialysis permits detection of increases and decreases in dopamine uptake in mouse nucleus accumbens. J. Neurosci. Methods 155, 187–193. - PubMed
-
- Bungay P. M.; Morrison P. F.; Dedrick R. L. (1990) Steady-state theory for quantitative microdialysis of solutes and water in vivo and in vitro. Life Sci. 46, 105–119. - PubMed
-
- Yim H. J.; Gonzales R. A. (2000) Ethanol-induced increases in dopamine extracellular concentration in rat nucleus accumbens are accounted for by increased release and not uptake inhibition. Alcohol 22, 107–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

