Architecture and membrane interactions of the EGF receptor
- PMID: 23374350
- PMCID: PMC3680629
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.12.030
Architecture and membrane interactions of the EGF receptor
Abstract
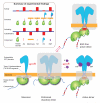
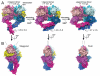
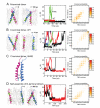
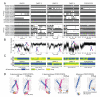
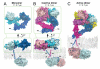
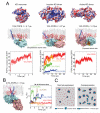
Dimerization-driven activation of the intracellular kinase domains of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) upon extracellular ligand binding is crucial to cellular pathways regulating proliferation, migration, and differentiation. Inactive EGFR can exist as both monomers and dimers, suggesting that the mechanism regulating EGFR activity may be subtle. The membrane itself may play a role but creates substantial difficulties for structural studies. Our molecular dynamics simulations of membrane-embedded EGFR suggest that, in ligand-bound dimers, the extracellular domains assume conformations favoring dimerization of the transmembrane helices near their N termini, dimerization of the juxtamembrane segments, and formation of asymmetric (active) kinase dimers. In ligand-free dimers, by holding apart the N termini of the transmembrane helices, the extracellular domains instead favor C-terminal dimerization of the transmembrane helices, juxtamembrane segment dissociation and membrane burial, and formation of symmetric (inactive) kinase dimers. Electrostatic interactions of EGFR's intracellular module with the membrane are critical in maintaining this coupling.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bessman NJ, Lemmon MA. Finding the missing links in EGFR. Nat. Struct. and Mol. Biol. 2012;19:1–3. - PubMed
-
- Bocharov EV, Mineev KS, Volynsky PE, Ermolyuk YS, Tkach EN, Sobol AG, Chupin VV, Kirpichnikov MP, Efremov RG, Arseniev AS. Spatial structure of the dimeric transmembrane domain of the growth factor receptor ErbB2 presumably corresponding to the receptor active state. J. Biol. Chem. 2008;283:6950–6956. - PubMed
-
- Cho HS, Leahy DJ. Structure of the extracellular region of HER3 reveals an interdomain tether. Science. 2002;297:1330–1333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

