High levels of γ-glutamyl hydrolase (GGH) are associated with poor prognosis and unfavorable clinical outcomes in invasive breast cancer
- PMID: 23374458
- PMCID: PMC3576262
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-47
High levels of γ-glutamyl hydrolase (GGH) are associated with poor prognosis and unfavorable clinical outcomes in invasive breast cancer
Abstract
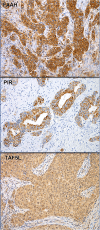
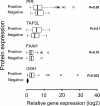
Background: Previously, we performed analysis of gene expression in 46 axillary lymph node negative tumors and identified molecular gene signatures that resulted in different clinical outcomes. The aim of this study was to determine the correlation of γ-glutamyl hydrolase (GGH), fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), Pirin (PIR) and TAF5-like RNA polymerase II, p300/CBP-associated factor (PCAF)-associated factor, 65 kDa (TAF5L), selected from identified gene signatures, with clinical outcomes as well as classical clinicopathological characteristics in primary invasive breast cancer patients.
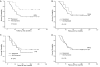
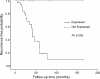
Methods: The protein levels of GGH, FAAH, PIR and TAF5L were assessed by immunohistochemistry (IHC) on a panel of 80 primary invasive breast tumors. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and western blot analysis were performed to verify the expression levels of the candidate biomarkers. Patient disease-specific survival (DSS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) were evaluated using the Kaplan-Meier method. The prognostic biomarkers were identified by univariate analysis with a log-rank test and by multivariate analysis with Cox proportional hazards regression models.
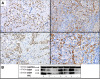
Results: The GGH and FAAH protein levels were significantly up-regulated in invasive breast cancer tumors compared with adjacent non-cancerous tissues. Furthermore, the protein levels of GGH and FAAH were significantly correlated in tumor tissues. Tumoral GGH protein expression was significantly correlated with shorter DSS and RFS. Furthermore, the protein expression of GGH was positively correlated with undifferentiated tumors (BRE grade III) and ER/PR expressing tumors. Multivariate regression analysis showed that only GGH protein expression independently predicts DSS. No such correlations were found for FAAH, PIR and TAF5L protein expression. However, elevated protein levels of FAAH were positively associated with high number of lymph node involvement and upregulated levels of PIR were positively related with lymph node metastasis. The TAF5L was pronouncedly down-regulated in primary invasive breast cancer tissues compared to matched adjacent non-cancerous tissues.
Conclusion: These data show for the first time that cytoplasmic GGH might play a relevant role in the development and progression of invasive breast cancer, warranting further investigations. Our findings suggest that GGH serve as a potential biomarker of unfavorable clinical outcomes over short-term follow-up in breast cancer. The GGH may be a very attractive targeted therapy for selected patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elevated cyclin B2 expression in invasive breast carcinoma is associated with unfavorable clinical outcome.BMC Cancer. 2013 Jan 2;13:1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-1. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23282137 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of TNFAIP8 is associated with tumor aggressiveness and poor prognosis in patients with invasive ductal breast carcinoma.Hum Pathol. 2017 Apr;62:40-49. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2016.12.020. Epub 2017 Jan 10. Hum Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28087477
-
Both high expression of pyruvate kinase M2 and vascular endothelial growth factor-C predicts poorer prognosis in human breast cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jul 1;8(7):8028-37. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26339369 Free PMC article.
-
Multicentric and multifocal versus unifocal breast cancer: is the tumor-node-metastasis classification justified?Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010 Jul;122(1):27-34. doi: 10.1007/s10549-010-0917-9. Epub 2010 May 8. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010. PMID: 20454925 Review.
-
Expression of YES-associated protein (YAP) and its clinical significance in breast cancer tissues.Hum Pathol. 2017 Oct;68:166-174. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2017.08.032. Epub 2017 Sep 9. Hum Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28899737 Review.
Cited by
-
Elevated Expression of Gamma-Glutamyl Hydrolase Is Associated With Poor Prognosis and Altered Immune Signature in Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma.Front Genet. 2022 Jan 10;12:764194. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.764194. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35082830 Free PMC article.
-
High-Level γ-Glutamyl-Hydrolase (GGH) Expression is Linked to Poor Prognosis in ERG Negative Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jan 29;18(2):286. doi: 10.3390/ijms18020286. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28146062 Free PMC article.
-
The Endocannabinoid System as a Pharmacological Target for New Cancer Therapies.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 15;13(22):5701. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225701. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34830856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Pirin, an Oxidative Stress Sensor Protein, in Epithelial Carcinogenesis.Biology (Basel). 2021 Feb 4;10(2):116. doi: 10.3390/biology10020116. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33557375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-155, identified as anti-metastatic by global miRNA profiling of a metastasis model, inhibits cancer cell extravasation and colonization in vivo and causes significant signaling alterations.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 6;6(30):29224-39. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4942. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26317550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS. et al.Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98(19):10869–10874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.191367098. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pollard C, Nitz M, Baras A, Williams P, Moskaluk C, Theodorescu D. Genoproteomic mining of urothelial cancer suggests {gamma}-glutamyl hydrolase and diazepam-binding inhibitor as putative urinary markers of outcome after chemotherapy. Am J Pathol. 2009;175(5):1824–1830. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.090155. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

