Pregabalin suppresses nociceptive behavior and central sensitization in a rat trigeminal neuropathic pain model
- PMID: 23374941
- PMCID: PMC3575215
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpain.2012.11.005
Pregabalin suppresses nociceptive behavior and central sensitization in a rat trigeminal neuropathic pain model
Abstract
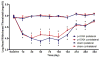
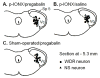
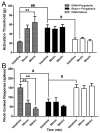
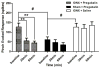
The aim of this study was to determine whether pregabalin affects nociceptive behavior and central sensitization in a trigeminal neuropathic pain model. A partial infraorbital nerve transection (p-IONX) or sham operation was performed in adult male rats. Nociceptive withdrawal thresholds were tested with von Frey filaments applied to the bilateral vibrissal pads pre- and postoperatively. On postoperative day 7, the behavioral assessment was conducted before and at 30, 60, 120, and 180 minutes after and 24 hours after pregabalin (.1, 1, 10, 100 mg/kg intraperitoneally) or saline injection. The effects of pregabalin or saline were also examined on the mechanoreceptive field and response properties of nociceptive neurons recorded in the medullary dorsal horn at postoperative days 7 to 10. Reduced withdrawal thresholds reflecting bilateral mechanical allodynia were observed in p-IONX rats until postoperative day 28, but not in sham-operated rats. At postoperative day 7, pregabalin significantly and dose-dependently reversed the reduced mechanical withdrawal thresholds in p-IONX rats. Pregabalin also attenuated central sensitization of the neurons, as reflected in reversal of their reduced activation threshold, increased responses to pinch/pressure, and enhanced stimulus-response function. This study provides the first documentation that pregabalin attenuates the mechanical allodynia and central sensitization that characterize this trigeminal neuropathic pain model, and supports its clinical use for treating craniofacial neuropathic pain.
Perspective: Trigeminal nerve injury in rats produced facial mechanical hypersensitivity and trigeminal central sensitization of medullary dorsal horn neurons that were markedly attenuated by systemically administered pregabalin, suggesting its potential clinical utility for orofacial neuropathic pain.
Copyright © 2013 American Pain Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The gap junction blocker carbenoxolone attenuates nociceptive behavior and medullary dorsal horn central sensitization induced by partial infraorbital nerve transection in rats.Pain. 2014 Feb;155(2):429-435. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.11.004. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Pain. 2014. PMID: 24239671 Free PMC article.
-
(-)-α-Bisabolol reduces nociception and trigeminal central sensitisation in acute orofacial neuropathic pain induced by infraorbital nerve injury.Life Sci. 2019 Jun 15;227:122-128. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.032. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31002923
-
Systemic pregabalin attenuates facial hypersensitivity and noxious stimulus-evoked release of glutamate in medullary dorsal horn in a rodent model of trigeminal neuropathic pain.Neurochem Int. 2013 May;62(6):831-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.02.022. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Neurochem Int. 2013. PMID: 23454190 Free PMC article.
-
Orofacial pain models induce impairment in spatial learning and working memory in rodents: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 5;988:177225. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.177225. Epub 2024 Dec 29. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39740736
-
Trigemino-hypoglossal somatic reflex in the pharmacological studies of nociception in orofacial area.Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2015;75(3):253-63. doi: 10.55782/ane-2015-2032. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2015. PMID: 26581382 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenic Mechanism of Dry Eye-Induced Chronic Ocular Pain and a Mechanism-Based Therapeutic Approach.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022 Jan 3;63(1):7. doi: 10.1167/iovs.63.1.7. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022. PMID: 34989761 Free PMC article.
-
The gap junction blocker carbenoxolone attenuates nociceptive behavior and medullary dorsal horn central sensitization induced by partial infraorbital nerve transection in rats.Pain. 2014 Feb;155(2):429-435. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.11.004. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Pain. 2014. PMID: 24239671 Free PMC article.
-
Descending serotonergic modulation from rostral ventromedial medulla to spinal trigeminal nucleus is involved in experimental occlusal interference-induced chronic orofacial hyperalgesia.J Headache Pain. 2023 May 10;24(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s10194-023-01584-3. J Headache Pain. 2023. PMID: 37165344 Free PMC article.
-
Pregabalin Failed to Prevent Dry Eye Symptoms after Laser-Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis (LASIK) in a Randomized Pilot Study.J Clin Med. 2019 Sep 1;8(9):1355. doi: 10.3390/jcm8091355. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31480601 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Molecular Targets for Treating Neuropathic Orofacial Pain Based on Current Findings in Animal Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 15;22(12):6406. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126406. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34203854 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahn DK, Lim EJ, Kim BC, Yang GY, Lee MK, Ju JS, Han SR, Bae YC. Compression of the trigeminal ganglion produces prolonged nociceptive behavior in rats. Eur J Pain. 2009;13:568–575. - PubMed
-
- Arnold LM, Goldenberg DL, Stanford SB, Lalonde JK, Sandhu HS, Keck PE, Jr, Welge JA, Bishop F, Stanford KE, Hess EV, Hudson JI. Gabapentin in the treatment of fibromyalgia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:1336–1344. - PubMed
-
- Cao Y, Wang H, Chiang CY, Dostrovsky JO, Sessle BJ. Effects of pregabalin on nociceptive behaviour and central sensitization in a trigeminal neuropathic pain model. Society for Neuroscience Meeting; 2011. p. Abstract No 72.27.
-
- Chen SR, Xu Z, Pan HL. Stereospecific effect of pregabalin on ectopic afferent discharges and neuropathic pain induced by sciatic nerve ligation in rats. Anesthesiology. 2001;95:1473–1479. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

