Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylases as targets for neuroprotection by "antioxidant" metal chelators: From ferroptosis to stroke
- PMID: 23376032
- PMCID: PMC4327984
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.01.026
Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylases as targets for neuroprotection by "antioxidant" metal chelators: From ferroptosis to stroke
Abstract
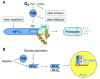
Neurologic conditions including stroke, Alzheimer disease, Parkinson disease, and Huntington disease are leading causes of death and long-term disability in the United States, and efforts to develop novel therapeutics for these conditions have historically had poor success in translating from bench to bedside. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α mediates a broad, evolutionarily conserved, endogenous adaptive program to hypoxia, and manipulation of components of the HIF pathway is neuroprotective in a number of human neurological diseases and experimental models. In this review, we discuss molecular components of one aspect of hypoxic adaptation in detail and provide perspective on which targets within this pathway seem to be ripest for preventing and repairing neurodegeneration. Further, we highlight the role of HIF prolyl hydroxylases as emerging targets for the salutary effects of metal chelators on ferroptosis in vitro as well in animal models of neurological diseases.
Keywords: Free radicals; Hypoxia-inducible factors; Metal chelators; Neurodegeneration; Prolyl hydroxylases; Transcription.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Ryu H, Lee J, Olofsson BA, Mwidau A, Dedeoglu A, Escudero M, Flemington E, Azizkhan-Clifford J, Ferrante RJ, Ratan RR. Histone deacetylase inhibitors prevent oxidative neuronal death independent of expanded polyglutamine repeats via an Sp1-dependent pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:4281–4286. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Siddiq A, Ayoub IA, Chavez JC, Aminova L, Shah S, LaManna JC, Patton SM, Connor JR, Cherny RA, Volitakis I, Bush AI, Langsetmo I, Seeley T, Gunzler V, Ratan RR. Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl 4-hydroxylase inhibition. A target for neuroprotection in the central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:41732–41743. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

