Dendritic cells: an important link between antiphospholipid antibodies, endothelial dysfunction, and atherosclerosis in autoimmune and non-autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 23376063
- PMCID: PMC3904226
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2012.12.002
Dendritic cells: an important link between antiphospholipid antibodies, endothelial dysfunction, and atherosclerosis in autoimmune and non-autoimmune diseases
Abstract
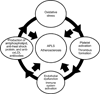
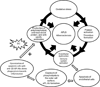
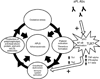
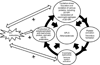
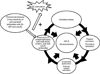
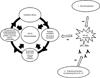
The presence of dendritic cells, antigen-presenting cells that link innate and adaptive immunity, is necessary to generate and maintain the production of antiphospholipid antibodies in response to exposed intracellular phospholipids on the outer surface of apoptotic cells. In turn, antiphospholipid antibodies enhance dendritic cell-induced inflammatory and proatherogenic responses in a number of conditions that are associated with accelerated atherosclerosis, including diabetes, chronic kidney disease, periodontal infections, and aging. While altering dendritic cells by modifying the ubiquitin-proteasome system enhances antiphospholipid antibody production and leads to development of accelerated atherosclerosis and autoimmune features, inducing tolerance by dendritic cell manipulation leads to decreased atherosclerosis and thrombosis. Therefore, further translational studies are needed to understand the interplay between dendritic cells and antiphospholipid antibodies, and to develop potential new therapies for antiphospholipid syndrome and atherosclerosis. Here we review current experimental and translational studies that have examined the role of dendritic cells in antiphospholipid antibody formation and in antiphospholipid-associated atherosclerosis and thrombosis.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Petri M. Epidemiology of the antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. J Autoimmun. 2000;15:145–151. - PubMed
-
- Levine JS, Branch DW, Rauch J. The antiphospholipid syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:752–763. - PubMed
-
- Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, Branch DW, Brey RL, Cervera R, Derksen RH, PG DEG, Koike T, Meroni PL, Reber G, Shoenfeld Y, Tincani A, Vlachoyiannopoulos PG, Krilis SA. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4:295–306. - PubMed
-
- Meroni PL, Borghi MO, Raschi E, Tedesco F. Pathogenesis of antiphospholipid syndrome: understanding the antibodies. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7:330–339. - PubMed
-
- Pierangeli SS, Chen PP, Raschi E, Scurati S, Grossi C, Borghi MO, Palomo I, Harris EN, Meroni PL. Antiphospholipid antibodies and the antiphospholipid syndrome: pathogenic mechanisms. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2008;34:236–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

