Elimination and utilization of oxidized guanine nucleotides in the synthesis of RNA and its precursors
- PMID: 23376345
- PMCID: PMC3605631
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.418723
Elimination and utilization of oxidized guanine nucleotides in the synthesis of RNA and its precursors
Abstract
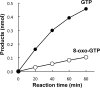
Reactive oxygen species are produced as side products of oxygen utilization and can lead to the oxidation of nucleic acids and their precursor nucleotides. Among the various oxidized bases, 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine seems to be the most critical during the transfer of genetic information because it can pair with both cytosine and adenine. During the de novo synthesis of guanine nucleotides, GMP is formed first, and it is converted to GDP by guanylate kinase. This enzyme hardly acts on an oxidized form of GMP (8-oxo-GMP) formed by the oxidation of GMP or by the cleavage of 8-oxo-GDP and 8-oxo-GTP by MutT protein. Although the formation of 8-oxo-GDP from 8-oxo-GMP is thus prevented, 8-oxo-GDP itself may be produced by the oxidation of GDP by reactive oxygen species. The 8-oxo-GDP thus formed can be converted to 8-oxo-GTP because nucleoside-diphosphate kinase and adenylate kinase, both of which catalyze the conversion of GDP to GTP, do not discriminate 8-oxo-GDP from normal GDP. The 8-oxo-GTP produced in this way and by the oxidation of GTP can be used for RNA synthesis. This misincorporation is prevented by MutT protein, which has the potential to cleave 8-oxo-GTP as well as 8-oxo-GDP to 8-oxo-GMP. When (14)C-labeled 8-oxo-GTP was applied to CaCl2-permeabilized cells of a mutT(-) mutant strain, it could be incorporated into RNA at 4% of the rate for GTP. Escherichia coli cells appear to possess mechanisms to prevent misincorporation of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine into RNA.
Figures

References
-
- Bjelland S., Seeberg E. (2003) Mutagenicity, toxicity and repair of DNA base damage induced by oxidation. Mutat. Res. 531, 37–80 - PubMed
-
- Imlay J. A. (2003) Pathways of oxidative damage. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 57, 395–418 - PubMed
-
- Nakatsu Y., Sekiguchi M. (2006) Oxidative Damage to Nucleotides: Consequences and Preventive Mechanisms. Oxidative Stress, Disease and Cancer, pp. 221–252, Imperial College Press, London
-
- Grollman A. P., Moriya M. (1993) Mutagenesis by 8-oxoguanine: an enemy within. Trends Genet. 9, 246–249 - PubMed
-
- Kuchino Y., Mori F., Kasai H., Inoue H., Iwai S., Miura K., Ohtsuka E., Nishimura S. (1987) Misreading of DNA templates containing 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine at the modified base and at adjacent residues. Nature 327, 77–79 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

