Akt and mTORC1 have different roles during liver tumorigenesis in mice
- PMID: 23376645
- PMCID: PMC3633657
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.01.053
Akt and mTORC1 have different roles during liver tumorigenesis in mice
Abstract
Background & aims: Phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) is deregulated in many human tumor types, including primary liver malignancies. The kinase v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1 (Akt) and mammalian target of rapamycin complex (mTORC1) are effectors of PI3K that promote cell growth and survival, but their individual roles in tumorigenesis are not well defined.
Methods: In livers of albumin (Alb)-Cre mice, we selectively deleted tuberous sclerosis (Tsc)1, a negative regulator of Ras homolog enriched in brain and mTORC1, along with Phosphatase and tensin homolog (Pten), a negative regulator of PI3K. Tumor tissues were characterized by histologic and biochemical analyses.
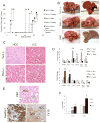
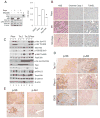
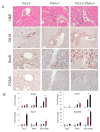
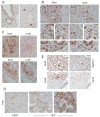
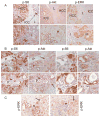
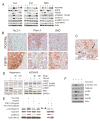
Results: The Tsc1fl/fl;AlbCre, Ptenfl/fl;AlbCre, and Tsc1fl/fl;Ptenfl/fl;AlbCre mice developed liver tumors that differed in size, number, and histologic features. Livers of Tsc1fl/fl;AlbCre mice did not develop steatosis; tumors arose later than in the other strains of mice and were predominantly hepatocellular carcinomas. Livers of the Ptenfl/fl;AlbCre mice developed steatosis and most of the tumors that formed were intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas. Livers of Tsc1fl/fl;Ptenfl/fl;AlbCre formed large numbers of tumors, of mixed histologies, with the earliest onset of any strain, indicating that loss of Tsc1 and Pten have synergistic effects on tumorigenesis. In these mice, the combination of rapamycin and MK2206 was more effective in reducing liver cell proliferation and inducing cell death than either reagent alone. Tumor differentiation correlated with Akt and mTORC1 activities; the ratio of Akt:mTORC1 activity was high throughout the course of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas development and low during hepatocellular carcinoma development. Compared with surrounding nontumor liver tissue, tumors from all 3 strains had increased activities of Akt, mTORC1, and mitogen-activated protein kinase and overexpressed fibroblast growth factor receptor 1. Inhibition of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 in Tsc1-null mice suppressed Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase activities in tumor cells.
Conclusions: Based on analyses of knockout mice, mTORC1 and Akt have different yet synergistic effects during the development of liver tumors in mice.
Copyright © 2013 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Zucman-Rossi J. Molecular classification of hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Liver Dis. 2010 Jul;42(Suppl 3):S235–241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

