Dicer-independent processing of short hairpin RNAs
- PMID: 23376931
- PMCID: PMC3616727
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt036
Dicer-independent processing of short hairpin RNAs
Abstract
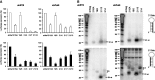
Short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) are widely used to induce RNA interference (RNAi). We tested a variety of shRNAs that differed in stem length and terminal loop size and revealed strikingly different RNAi activities and shRNA-processing patterns. Interestingly, we identified a specific shRNA design that uses an alternative Dicer-independent processing pathway. Detailed analyses indicated that a short shRNA stem length is critical for avoiding Dicer processing and activation of the alternative processing route, in which the shRNA is incorporated into RISC and processed by the AGO2-mediated slicer activity. Such alternatively processed shRNAs (AgoshRNAs) yield only a single RNA strand that effectively induces RNAi, whereas conventional shRNA processing results in an siRNA duplex of which both strands can trigger RNAi. Both the processing and subsequent RNAi activity of these AgoshRNAs are thus mediated by the RISC-component AGO2. These results have important implications for the future design of more specific RNAi therapeutics.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Probing the shRNA characteristics that hinder Dicer recognition and consequently allow Ago-mediated processing and AgoshRNA activity.RNA. 2014 Sep;20(9):1410-8. doi: 10.1261/rna.043950.113. Epub 2014 Jul 17. RNA. 2014. PMID: 25035295 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic insights on the Dicer-independent AGO2-mediated processing of AgoshRNAs.RNA Biol. 2015;12(1):92-100. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1017204. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 25826416 Free PMC article.
-
Toward optimization of AgoshRNA molecules that use a non-canonical RNAi pathway: variations in the top and bottom base pairs.RNA Biol. 2015;12(4):447-56. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1022024. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 25747107 Free PMC article.
-
Dicer-independent processing of small RNA duplexes: mechanistic insights and applications.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Oct 13;45(18):10369-10379. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx779. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28977573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Components and assembly of RNA-induced silencing complex].Yi Chuan. 2006 Jun;28(6):761-6. Yi Chuan. 2006. PMID: 16818443 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Optimal delivery of RNA interference by viral vectors for cancer therapy.Mol Ther. 2023 Nov 1;31(11):3127-3145. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.09.012. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Mol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37735876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probing the shRNA characteristics that hinder Dicer recognition and consequently allow Ago-mediated processing and AgoshRNA activity.RNA. 2014 Sep;20(9):1410-8. doi: 10.1261/rna.043950.113. Epub 2014 Jul 17. RNA. 2014. PMID: 25035295 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation of nucleotides around the +1 position of type 3 polymerase III promoters: The effect on transcriptional activity and start site usage.Transcription. 2017;8(5):275-287. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2017.1322170. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Transcription. 2017. PMID: 28598252 Free PMC article.
-
Guidelines for the optimal design of miRNA-based shRNAs.Methods. 2016 Jul 1;103:157-66. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2016.04.003. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Methods. 2016. PMID: 27083402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Silico Prediction and Selection of Target Sequences in the SARS-CoV-2 RNA Genome for an Antiviral Attack.Viruses. 2022 Feb 14;14(2):385. doi: 10.3390/v14020385. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215977 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, Hannon GJ. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature. 2001;409:363–366. - PubMed
-
- Nykanen A, Haley B, Zamore PD. ATP requirements and small interfering RNA structure in the RNA interference pathway. Cell. 2001;107:309–321. - PubMed
-
- Denli AM, Tops BB, Plasterk RH, Ketting RF, Hannon GJ. Processing of primary microRNAs by the microprocessor complex. Nature. 2004;432:231–235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

