Finding the sources of missing heritability in a yeast cross
- PMID: 23376951
- PMCID: PMC4001867
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11867
Finding the sources of missing heritability in a yeast cross
Abstract
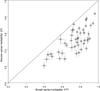
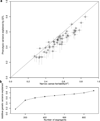
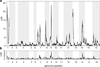
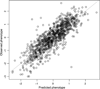
For many traits, including susceptibility to common diseases in humans, causal loci uncovered by genetic-mapping studies explain only a minority of the heritable contribution to trait variation. Multiple explanations for this 'missing heritability' have been proposed. Here we use a large cross between two yeast strains to accurately estimate different sources of heritable variation for 46 quantitative traits, and to detect underlying loci with high statistical power. We find that the detected loci explain nearly the entire additive contribution to heritable variation for the traits studied. We also show that the contribution to heritability of gene-gene interactions varies among traits, from near zero to approximately 50 per cent. Detected two-locus interactions explain only a minority of this contribution. These results substantially advance our understanding of the missing heritability problem and have important implications for future studies of complex and quantitative traits.
Figures
Comment in
-
Complex traits: Missing in action.Nat Rev Genet. 2013 Apr;14(4):237. doi: 10.1038/nrg3447. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Nat Rev Genet. 2013. PMID: 23419279 No abstract available.
References
Additional References
-
- Amberg DC, Burke D, Strathern JN. Methods in yeast genetics : a Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory course manual. xvii. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2005. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; p. 230.
-
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2012.
-
- Broman KW, Wu H, Sen S, Churchill GA. R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:889–890. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

