O death where is thy sting? Immunologic tolerance to apoptotic self
- PMID: 23377225
- PMCID: PMC3679293
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-013-1261-0
O death where is thy sting? Immunologic tolerance to apoptotic self
Abstract
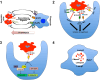
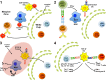
In higher organisms, innate scavenging cells maintain physiologic homeostasis by removal of the billions of apoptotic cells generated on a daily basis. Apoptotic cell removal requires efficient recognition and uptake by professional and non-professional phagocytic cells, which are governed by an array of soluble and apoptotic cell-integral signals resulting in immunologically silent clearance. While apoptosis is associated with profound suppression of adaptive and innate inflammatory immunity, we have only begun to scratch the surface in understanding how immunologic tolerance to apoptotic self manifest at either the molecular or cellular level. In the last 10 years, data has emerged implicating professional phagocytes, most notably stromal macrophages and CD8α(+)CD103(+) dendritic cells, as critical in initiation of the regulatory cascade that will ultimately lead to long-term whole-animal immune tolerance. Importantly, recent work by our lab and others has shown that alterations in apoptotic cell perception by the innate immune system either by removal of critical phagocytic sentinels in secondary lymphoid organs or blockage of immunosuppressive pathways leads to pronounced inflammation with a breakdown of tolerance towards self. This challenges the paradigm that apoptotic cells are inherently immunosuppressive, suggesting that apoptotic cell tolerance is a "context-dependent" event.
Figures
References
-
- Platt N, Suzuki H, Kodama T, Gordon S. Apoptotic thymocyte clearance in scavenger receptor class A-deficient mice is apparently normal. J Immunol. 2000;164(9):4861–4867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

