Transthoracic bioimpedance and brain natriuretic peptide assessment for prognostic stratification of outpatients with chronic systolic heart failure
- PMID: 23377871
- PMCID: PMC6649445
- DOI: 10.1002/clc.22086
Transthoracic bioimpedance and brain natriuretic peptide assessment for prognostic stratification of outpatients with chronic systolic heart failure
Abstract
Background: In patients with chronic heart failure, physical evaluation and clinical judgment may be inadequate for prognostic stratification.
Hypothesis: Information obtained with simple bedside tests would be helpful in patient management.
Methods: We report on 142 outpatients with systolic heart failure seen at our heart failure unit from 2007 to 2010 (ages 69.4 ± 8.9 years; ejection fraction [EF] 30.6 ± 6.1%; 43% with implanted defibrillators and/or resynchronization devices). At their first visit, we assessed levels of brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) (pg/mL), evaluated transthoracic conductance (TFC) (1/kΩ) by transthoracic bioimpedance, and performed echocardiography.
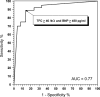
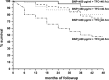
Results: Four-year mortality was 21.2%. At multivariate analysis, surviving and deceased subjects did not differ regarding New York Heart Association, age, gender, heart failure etiology, or EF at index visit. Patients who died had higher BNP and TFC (BNP = 884 ± 119 pg/mL vs 334 ± 110 pg/mL; TFC = 50 ± 8/kΩ vs 37 ± 7/kΩ, both P < 0.001]. Patients with BNP < 450 pg/mL and TFC < 40/kΩ had a 2.1% 4-year mortality, compared to 46.5% mortality of patients having BNP ≥ 450 pg/mL and TFC ≥ 40/kΩ. BNP ≥ 450 pg/mL and TFC ≥ 40/kΩ showed high sensitivity (91%) and specificity (88%)in identifying patients who died at follow-up.
Conclusions: The combined use of BNP and impedance cardiography during the first assessment of a patient in a heart failure unit identified those carrying a worse medium-term prognosis. This approach could help the subsequent management of patients, allowing better clinical and therapeutic strategies.
© 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Metra M, Ponikowski P, Dickstein K, et al; Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Advanced chronic heart failure: a position statement from the Study Group on Advanced Heart Failure of the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail. 2007;9:684–694. - PubMed
-
- Damman K, Voors AA, Hillege HL, et al; CIBIS‐2 Investigators and Committees. Congestion in chronic systolic heart failure is related to renal dysfunction and increased mortality. Eur J Heart Fail. 2010;12:974–982. - PubMed
-
- Gheorghiade M, Shin DD, Thomas TO, et al. Congestion is an important diagnostic and therapeutic target in heart failure. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2006;7(suppl 1):S12–S24. - PubMed
-
- The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2008 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association of the ESC (HFA) and endorsed by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM). ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008. Eur Heart J. 2008;29:2388–2442. - PubMed
-
- Lucas C, Johnson W, Hamilton MA, et al. Freedom from congestion predicts good survival despite previous class IV symptoms of heart failure. Am Heart J. 2000;140:840–847. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

