Lin28a regulates germ cell pool size and fertility
- PMID: 23378032
- PMCID: PMC3652309
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.1343
Lin28a regulates germ cell pool size and fertility
Abstract
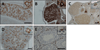
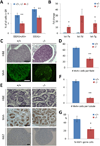
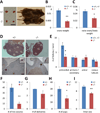
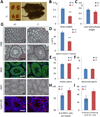
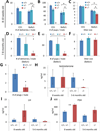
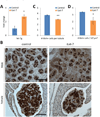
Overexpression of LIN28A is associated with human germ cell tumors and promotes primordial germ cell (PGC) development from embryonic stem cells in vitro and in chimeric mice. Knockdown of Lin28a inhibits PGC development in vitro, but how constitutional Lin28a deficiency affects the mammalian reproductive system in vivo remains unknown. Here, we generated Lin28a knockout (KO) mice and found that Lin28a deficiency compromises the size of the germ cell pool in both males and females by affecting PGC proliferation during embryogenesis. Interestingly however, in Lin28a KO males, the germ cell pool partially recovers during postnatal expansion, while fertility remains impaired in both males and females mated to wild-type mice. Embryonic overexpression of let-7, a microRNA negatively regulated by Lin28a, reduces the germ cell pool, corroborating the role of the Lin28a/let-7 axis in regulating the germ lineage.
Copyright © 2013 AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURE OF POTENTIAL CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RNA-binding protein TIAR is essential for primordial germ cell development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Mar 3;95(5):2331-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.5.2331. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9482885 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA biogenesis is required for mouse primordial germ cell development and spermatogenesis.PLoS One. 2008 Mar 5;3(3):e1738. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001738. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18320056 Free PMC article.
-
Lin28a is dormant, functional, and dispensable during mouse oocyte-to-embryo transition.Biol Reprod. 2014 Jun;90(6):131. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.114.118703. Epub 2014 May 14. Biol Reprod. 2014. PMID: 24829024
-
Spermatogonial stem cells: updates from specification to clinical relevance.Hum Reprod Update. 2019 May 1;25(3):275-297. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmz006. Hum Reprod Update. 2019. PMID: 30810745 Review.
-
[Nanos2 in the male reproductive system: Progress in studies].Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2018 Jun;24(6):558-561. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2018. PMID: 30173464 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
LIN28 Family in Testis: Control of Cell Renewal, Maturation, Fertility and Aging.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 29;23(13):7245. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137245. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UXT is required for spermatogenesis in mice.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 12;13(4):e0195747. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195747. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29649254 Free PMC article.
-
Lin28 sustains early renal progenitors and induces Wilms tumor.Genes Dev. 2014 May 1;28(9):971-82. doi: 10.1101/gad.237149.113. Epub 2014 Apr 14. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 24732380 Free PMC article.
-
Lin28a/let-7 pathway modulates the Hox code via Polycomb regulation during axial patterning in vertebrates.Elife. 2020 May 29;9:e53608. doi: 10.7554/eLife.53608. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32479258 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-binding proteins in human oogenesis: Balancing differentiation and self-renewal in the female fetal germline.Stem Cell Res. 2017 May;21:193-201. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2017.04.008. Epub 2017 Apr 18. Stem Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28434825 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ambros V, Horvitz HR. Heterochronic mutants of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 1984;226:409–416. - PubMed
-
- Moss EG, Lee RC, Ambros V. The cold shock domain protein LIN-28 controls developmental timing in C. elegans and is regulated by the lin-4 RNA. Cell. 1997;88:637–646. - PubMed
-
- Heo I, Joo C, Cho J, et al. Lin28 mediates the terminal uridylation of let-7 precursor MicroRNA. Mol Cell. 2008;32:276–284. - PubMed
-
- Rybak A, Fuchs H, Smirnova L, et al. A feedback loop comprising lin-28 and let-7 controls pre-let-7 maturation during neural stem-cell commitment. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:987–993. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

