DNA base damage by reactive oxygen species, oxidizing agents, and UV radiation
- PMID: 23378590
- PMCID: PMC3552502
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012559
DNA base damage by reactive oxygen species, oxidizing agents, and UV radiation
Abstract
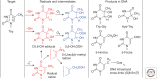
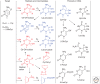
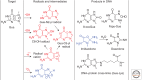
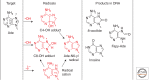
Emphasis has been placed in this article dedicated to DNA damage on recent aspects of the formation and measurement of oxidatively generated damage in cellular DNA in order to provide a comprehensive and updated survey. This includes single pyrimidine and purine base lesions, intrastrand cross-links, purine 5',8-cyclonucleosides, DNA-protein adducts and interstrand cross-links formed by the reactions of either the nucleobases or the 2-deoxyribose moiety with the hydroxyl radical, one-electron oxidants, singlet oxygen, and hypochlorous acid. In addition, recent information concerning the mechanisms of formation, individual measurement, and repair-rate assessment of bipyrimidine photoproducts in isolated cells and human skin upon exposure to UVB radiation, UVA photons, or solar simulated light is critically reviewed.
Figures
References
-
- Aida M, Nishimura S 1987. An ab initio molecular orbital study on the characteristics of 8-hydroxyguanine. Mut Res Lett 192: 83–89 - PubMed
-
- Asgatay S, Martinez A, Coantic-Castex S, Harakat D, Philippe C, Douki T, Clivio P 2010. UV-induced TA photoproducts: Formation and hydrolysis in double-stranded DNA. J Am Chem Soc 132: 10260–10261 - PubMed
-
- Azqueta A, Shaposhnikov S, Collins AR 2009. DNA oxidation: Investigating its key role in mutagenesis with the comet assay. Mutat Res 674: 101–108 - PubMed
-
- Badouard C, Masuda M, Nishino H, Cadet J, Favier A, Ravanat JL 2005. Detection of chlorinated DNA and RNA nucleosides by HPLC coupled to tandem mass spectrometry as potential biomarkers of inflammation. J Chromatogr B 827: 26–31 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
