A novel approach to oral apoA-I mimetic therapy
- PMID: 23378594
- PMCID: PMC3606004
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M033555
A novel approach to oral apoA-I mimetic therapy
Erratum in
- J Lipid Res. 2013 Nov;54(11):3220. Farias-Eisener, Robin [corrected to Farias-Eisener, Robin]
Abstract
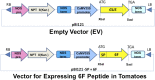
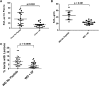
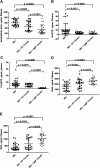
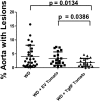
Transgenic tomato plants were constructed with an empty vector (EV) or a vector expressing an apoA-I mimetic peptide, 6F. EV or 6F tomatoes were harvested, lyophilized, ground into powder, added to Western diet (WD) at 2.2% by weight, and fed to LDL receptor-null (LDLR(-/-)) mice at 45 mg/kg/day 6F. After 13 weeks, the percent of the aorta with lesions was 4.1 ± 4%, 3.3 ± 2.4%, and 1.9 ± 1.4% for WD, WD + EV, and WD + 6F, respectively (WD + 6F vs. WD, P = 0.0134; WD + 6F vs. WD + EV, P = 0.0386; WD + EV vs. WD, not significant). While body weight did not differ, plasma serum amyloid A (SAA), total cholesterol, triglycerides, and lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) levels were less in WD + 6F mice; P < 0.0295. HDL cholesterol and paroxonase-1 activity (PON) were higher in WD + 6F mice (P = 0.0055 and P = 0.0254, respectively), but not in WD + EV mice. Plasma SAA, total cholesterol, triglycerides, LPA, and 15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (HETE) levels positively correlated with lesions (P < 0.0001); HDL cholesterol and PON were inversely correlated (P < 0.0001). After feeding WD + 6F: i) intact 6F was detected in small intestine (but not in plasma); ii) small intestine LPA was decreased compared with WD + EV (P < 0.0469); and iii) small intestine LPA 18:2 positively correlated with the percent of the aorta with lesions (P < 0.0179). These data suggest that 6F acts in the small intestine and provides a novel approach to oral apoA-I mimetic therapy.
Figures








Comment in
-
ApoA-I mimetics: tomatoes to the rescue.J Lipid Res. 2013 Apr;54(4):878-80. doi: 10.1194/jlr.E037572. Epub 2013 Mar 7. J Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23471030 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Navab M., Reddy S. T., Van Lenten B. J., Buga G. M., Hough G., Wagner A. C., Fogelman A. M. 2012. High-density lipoprotein and 4F peptide reduce systemic inflammation by modulating intestinal oxidized lipid metabolism: novel hypotheses and review of literature. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 32: 2553–2560. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

