Phosphorylation of phytochrome B inhibits light-induced signaling via accelerated dark reversion in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 23378619
- PMCID: PMC3608776
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.112.106898
Phosphorylation of phytochrome B inhibits light-induced signaling via accelerated dark reversion in Arabidopsis
Abstract
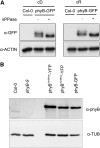
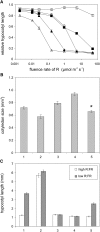
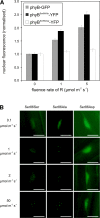
The photoreceptor phytochrome B (phyB) interconverts between the biologically active Pfr (λmax = 730 nm) and inactive Pr (λmax = 660 nm) forms in a red/far-red-dependent fashion and regulates, as molecular switch, many aspects of light-dependent development in Arabidopsis thaliana. phyB signaling is launched by the biologically active Pfr conformer and mediated by specific protein-protein interactions between phyB Pfr and its downstream regulatory partners, whereas conversion of Pfr to Pr terminates signaling. Here, we provide evidence that phyB is phosphorylated in planta at Ser-86 located in the N-terminal domain of the photoreceptor. Analysis of phyB-9 transgenic plants expressing phospho-mimic and nonphosphorylatable phyB-yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) fusions demonstrated that phosphorylation of Ser-86 negatively regulates all physiological responses tested. The Ser86Asp and Ser86Ala substitutions do not affect stability, photoconversion, and spectral properties of the photoreceptor, but light-independent relaxation of the phyB(Ser86Asp) Pfr into Pr, also termed dark reversion, is strongly enhanced both in vivo and in vitro. Faster dark reversion attenuates red light-induced nuclear import and interaction of phyB(Ser86Asp)-YFP Pfr with the negative regulator PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR3 compared with phyB-green fluorescent protein. These data suggest that accelerated inactivation of the photoreceptor phyB via phosphorylation of Ser-86 represents a new paradigm for modulating phytochrome-controlled signaling.
Figures


Comment in
-
Phosphorylation and dark reversion of phytochrome B.Plant Cell. 2013 Feb;25(2):358. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.250211. Epub 2013 Feb 12. Plant Cell. 2013. PMID: 23404884 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Differential phosphorylation of the N-terminal extension regulates phytochrome B signaling.New Phytol. 2020 Feb;225(4):1635-1650. doi: 10.1111/nph.16243. Epub 2019 Nov 7. New Phytol. 2020. PMID: 31596952
-
The Arabidopsis phytochrome-interacting factor PIF7, together with PIF3 and PIF4, regulates responses to prolonged red light by modulating phyB levels.Plant Cell. 2008 Feb;20(2):337-52. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.052142. Epub 2008 Feb 5. Plant Cell. 2008. PMID: 18252845 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation of phytochrome-B negatively regulates light-induced signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Sep 1;112(35):11108-13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1415260112. Epub 2015 Aug 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26283376 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochrome B phosphorylation expanded: site-specific kinases are identified.New Phytol. 2024 Jan;241(1):65-72. doi: 10.1111/nph.19314. Epub 2023 Oct 9. New Phytol. 2024. PMID: 37814506 Review.
-
Phytochrome B photobody components.New Phytol. 2024 May;242(3):909-915. doi: 10.1111/nph.19675. Epub 2024 Mar 13. New Phytol. 2024. PMID: 38477037 Review.
Cited by
-
Biological Significance of Photoreceptor Photocycle Length: VIVID Photocycle Governs the Dynamic VIVID-White Collar Complex Pool Mediating Photo-adaptation and Response to Changes in Light Intensity.PLoS Genet. 2015 May 15;11(5):e1005215. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005215. eCollection 2015 May. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25978382 Free PMC article.
-
Photobody Localization of Phytochrome B Is Tightly Correlated with Prolonged and Light-Dependent Inhibition of Hypocotyl Elongation in the Dark.Plant Physiol. 2014 Jun;165(2):595-607. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.236661. Epub 2014 Apr 25. Plant Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24769533 Free PMC article.
-
PCH1 and PCHL promote photomorphogenesis in plants by controlling phytochrome B dark reversion.Nat Commun. 2017 Dec 20;8(1):2221. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02311-8. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 29263319 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational Change of Tetratricopeptide Repeats Region Triggers Activation of Phytochrome-Associated Protein Phosphatase 5.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Oct 14;12:733069. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.733069. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34721460 Free PMC article.
-
Seedling Establishment: A Dimmer Switch-Regulated Process between Dark and Light Signaling.Plant Physiol. 2018 Feb;176(2):1061-1074. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.01460. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Plant Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29217596 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmad M., Jarillo J.A., Smirnova O., Cashmore A.R. (1998). The CRY1 blue light photoreceptor of Arabidopsis interacts with phytochrome A in vitro. Mol. Cell 1: 939–948 - PubMed
-
- Al-Sady B., Ni W.M., Kircher S., Schäfer E., Quail P.H. (2006). Photoactivated phytochrome induces rapid PIF3 phosphorylation prior to proteasome-mediated degradation. Mol. Cell 23: 439–446 - PubMed
-
- Bae G., Choi G. (2008). Decoding of light signals by plant phytochromes and their interacting proteins. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 59: 281–311 - PubMed
-
- Bauer D., Viczián A., Kircher S., Nobis T., Nitschke R., Kunkel T., Panigrahi K.C.S., Adám É., Fejes E., Schäfer E., Nagy F. (2004). Constitutive photomorphogenesis 1 and multiple photoreceptors control degradation of phytochrome interacting factor 3, a transcription factor required for light signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16: 1433–1445 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

