Urinary liver-type fatty acid-binding protein and progression of diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 23378622
- PMCID: PMC3687279
- DOI: 10.2337/dc12-1868
Urinary liver-type fatty acid-binding protein and progression of diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
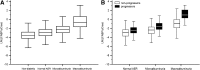
Objective: Diabetic nephropathy (DN) has mainly been considered a glomerular disease, although tubular dysfunction may also play a role. This study assessed the predictive value for progression of a tubular marker, urinary liver-type fatty acid-binding protein (L-FABP), at all stages of DN.
Research design and methods: At baseline, 1,549 patients with type 1 diabetes had an albumin excretion rate (AER) within normal reference ranges, 334 had microalbuminuria, and 363 had macroalbuminuria. Patients were monitored for a median of 5.8 years (95% CI 5.7-5.9). In addition, 208 nondiabetic subjects were studied. L-FABP was measured by ELISA and normalized with urinary creatinine. Different Cox proportional hazard models for the progression at every stage of DN were used to evaluate the predictive value of L-FABP. The potential benefit of using L-FABP alone or together with AER was assessed by receiver operating characteristic curve analyses.
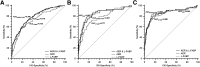
Results: L-FABP was an independent predictor of progression at all stages of DN. As would be expected, receiver operating characteristic curves for the prediction of progression were significantly larger for AER than for L-FABP, except for patients with baseline macroalbuminuria, in whom the areas were similar. Adding L-FABP to AER in the models did not significantly improve risk prediction of progression in favor of the combination of L-FABP plus AER compared with AER alone.
Conclusions: L-FABP is an independent predictor of progression of DN irrespective of disease stage. L-FABP used alone or together with AER may not improve the risk prediction of DN progression in patients with type 1 diabetes, but further studies are needed in this regard.
Figures
References
-
- Viberti GC, Hill RD, Jarrett RJ, Argyropoulos A, Mahmud U, Keen H. Microalbuminuria as a predictor of clinical nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1982;1:1430–1432 - PubMed
-
- Fioretto P, Steffes MW, Mauer M. Glomerular structure in nonproteinuric IDDM patients with various levels of albuminuria. Diabetes 1994;43:1358–1364 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

