Proinflammatory cytokines, adiponectin, and increased risk of primary cardiovascular events in diabetic patients with or without renal dysfunction: results from the ESTHER study
- PMID: 23378623
- PMCID: PMC3661844
- DOI: 10.2337/dc12-1416
Proinflammatory cytokines, adiponectin, and increased risk of primary cardiovascular events in diabetic patients with or without renal dysfunction: results from the ESTHER study
Abstract
Objective: Inflammatory processes contribute to both diabetes and cardiovascular risk. We wanted to investigate whether circulating concentrations of proinflammatory immune mediators and adiponectin in diabetic patients are associated with incident cardiovascular events.
Research design and methods: In 1,038 participants with diabetes of the population-based ESTHER study, of whom 326 showed signs of renal dysfunction, Cox proportional hazards models were used to estimate hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% CIs for the association of increasing concentrations of C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-18, macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF), adiponectin, and leptin with cardiovascular events (myocardial infarction, stroke, or fatal cardiovascular event) during a follow-up period of 8 years.
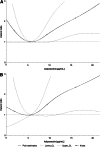
Results: During follow-up, 161 subjects with diabetes experienced a primary cardiovascular event. Proinflammatory markers were not associated with a higher risk for primary cardiovascular events in the total study population after adjustment for multiple confounders. However, IL-6 and MIF were associated with cardiovascular events in subjects with renal dysfunction (HR for the comparison of top vs. bottom tertile 1.98 [95% CI 1.12-3.52], P [trend] = 0.10 for IL-6; 1.48 [0.87-2.51], P [trend] = 0.04 for MIF). Adiponectin levels were associated with cardiovascular events in the total population (1.48 [1.01-2.21], P [trend] = 0.03), and the association was even more pronounced in the subgroup with renal dysfunction (1.97 [1.08-3.57], P [trend] = 0.02).
Conclusions: In particular, the absence of an association between CRP and a U-shaped association of adiponectin levels with incident cardiovascular events show that associations between circulating immune mediators and cardiovascular risk differ between diabetic patients and subjects of the general population.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Higher circulating omentin is associated with increased risk of primary cardiovascular events in individuals with diabetes.Diabetologia. 2020 Feb;63(2):410-418. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-05017-2. Epub 2019 Nov 9. Diabetologia. 2020. PMID: 31705160
-
The plasma leptin/adiponectin ratio predicts first cardiovascular event in men: a prospective nested case-control study.Eur J Intern Med. 2012 Dec;23(8):755-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2012.06.013. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Eur J Intern Med. 2012. PMID: 22819464
-
Overweight, hypertension and cardiovascular disease: focus on adipocytokines, insulin, weight changes and natriuretic peptides.Dan Med J. 2015 Nov;62(11):B5163. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 26522487
-
Interleukin-6 in the prediction of primary cardiovascular events in diabetes patients: results from the ESTHER study.Atherosclerosis. 2011 May;216(1):244-7. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.01.041. Epub 2011 Feb 2. Atherosclerosis. 2011. PMID: 21334625
-
Adipose tissue cytokines, insulin sensitivity, inflammation, and cardiovascular outcomes in end-stage renal disease patients.J Ren Nutr. 2005 Jan;15(1):125-30. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2004.09.036. J Ren Nutr. 2005. PMID: 15648021 Review.
Cited by
-
Lower Levels of Circulating Adiponectin in Elderly Patients with Metabolic Inflammatory Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020 Feb 28;13:591-596. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S242397. eCollection 2020. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020. PMID: 32184638 Free PMC article.
-
What Links an Increased Cardiovascular Risk and Inflammatory Bowel Disease? A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2021 Jul 30;13(8):2661. doi: 10.3390/nu13082661. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34444821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysing horizontal equity in enrolment in Disease Management Programmes for coronary heart disease in Germany 2008-2010.Int J Equity Health. 2015 Mar 10;14:28. doi: 10.1186/s12939-015-0155-1. Int J Equity Health. 2015. PMID: 25879523 Free PMC article.
-
Smoking-Associated DNA Methylation Biomarkers and Their Predictive Value for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality.Environ Health Perspect. 2016 Jan;124(1):67-74. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1409020. Epub 2015 May 27. Environ Health Perspect. 2016. PMID: 26017925 Free PMC article.
-
Cohort profile: the German Diabetes Study (GDS).Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2016 Apr 7;15:59. doi: 10.1186/s12933-016-0374-9. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2016. PMID: 27053136 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Curb JD, Abbott RD, Rodriguez BL, et al. C-reactive protein and the future risk of thromboembolic stroke in healthy men. Circulation 2003;107:2016–2020 - PubMed
-
- Best LG, Zhang Y, Lee ET, et al. C-reactive protein as a predictor of cardiovascular risk in a population with a high prevalence of diabetes: the Strong Heart Study. Circulation 2005;112:1289–1295 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous