A generalized G-SFED continuum solvation free energy calculation model
- PMID: 23378634
- PMCID: PMC3581891
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1221940110
A generalized G-SFED continuum solvation free energy calculation model
Abstract
An empirical continuum solvation model, solvation free energy density (SFED), has been developed to calculate solvation free energies of a molecule in the most frequently used solvents. A generalized version of the SFED model, generalized-SFED (G-SFED), is proposed here to calculate molecular solvation free energies in virtually any solvent. G-SFED provides an accurate and fast generalized framework without a complicated description of a solution. In the model, the solvation free energy of a solute is represented as a linear combination of empirical functions of the solute properties representing the effects of solute on various solute-solvent interactions, and the complementary solvent effects on these interactions were reflected in the linear expansion coefficients with a few solvent properties. G-SFED works well for a wide range of sizes and polarities of solute molecules in various solvents as shown by a set of 5,753 solvation free energies of diverse combinations of 103 solvents and 890 solutes. Octanol-water partition coefficients of small organic compounds and peptides were calculated with G-SFED with accuracy within 0.4 log unit for each group. The G-SFED computation time depends linearly on the number of nonhydrogen atoms (n) in a molecule, O(n).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
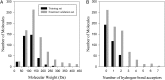
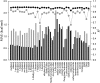
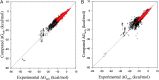
 . Red and black dots represent the solvation free energies in the training and external validation sets, respectively. The MAEs and R2s were 0.73 kcal/cal and 0.95, respectively, for G-SFED, and 0.90 kcal/mol and 0.89, respectively, for SM.42R.
. Red and black dots represent the solvation free energies in the training and external validation sets, respectively. The MAEs and R2s were 0.73 kcal/cal and 0.95, respectively, for G-SFED, and 0.90 kcal/mol and 0.89, respectively, for SM.42R.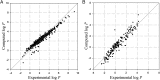
References
-
- Mahato RI, Narang AS, Thoma L, Miller DD. Emerging trends in oral delivery of peptide and protein drugs. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2003;20(2-3):153–214. - PubMed
-
- Fjell CD, Hiss JA, Hancock REW, Schneider G. Designing antimicrobial peptides: Form follows function. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012;11(1):37–51. - PubMed
-
- Ángyán JG. Common theoretical framework for quantum chemical solvent effect theories. J Meth Phys. 1992;10:93–137.
-
- Tomasi J, Persico M. Molecular interactions in solution: An overview of methods based on continuous distributions of the solvent. Chem Rev. 1994;94(7):2027–2094.
-
- Smith PE, Pettitt BM. Modeling solvent in biomolecular systems. J Phys Chem. 1994;98(39):9700–9711.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

