Lack of iGb3 and Isoglobo-Series Glycosphingolipids in Pig Organs Used for Xenotransplantation: Implications for Natural Killer T-Cell Biology
- PMID: 23378701
- PMCID: PMC3558945
- DOI: 10.1080/07328303.2012.741637
Lack of iGb3 and Isoglobo-Series Glycosphingolipids in Pig Organs Used for Xenotransplantation: Implications for Natural Killer T-Cell Biology
Abstract
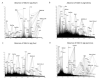
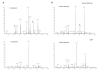
α-1,3-Terminated galactose residues on glycoproteins and glycosphingolipids are recognized by natural anti-α-1,3-galactose antibodies in human serum and cause hyperacute rejection in pig-to-human xenotransplantation. Genetic depletion of α-1,3-galactosyltransferase-1 in pigs abolishes the hyperacute rejection reaction. However, the isoglobotriosylceramide (iGb3) synthase in pigs may produce additional α-1,3-terminated galactose residues on glycosphingolipids. In both α-1,3-galactosyltranserase-1 knockout mice and pigs, cytotoxic anti-α-1,3-galactose antibodies could be induced; thus, a paradox exists that anti-α-1,3-galactose antibodies are present in animals with functional iGb3 synthases. Furthermore, iGb3 has been found to be an endogenous antigen for natural killer T (NKT) cells, an innate type of lymphocyte that may initiate the adaptive immune responses. It has been reasoned that iGb3 may trigger the activation of NKT cells and cause the rejection of α-1,3-galactosyltransferase-1-deficient organs through the potent stimulatory effects of NKT cells on adaptive immune cells (see ref.([20])). In this study, we examined the expression of iGb3 and the isoglobo-series glycosphingolipids in pig organs, including the heart, liver, pancreas, and kidney, by ion-trap mass spectrometry, which has a sensitivity of measuring 1% iGb3 among Gb3 isomers, when 5 μg/mL of the total iGb3/Gb3 mixture is present (see ref.([35])). We did not detect iGb3 or other isoglobo-series glycosphingolipids in any of these organs, although they were readily detected in mouse and human thymus and dendritic cells. The lack of iGb3 and isoglobo-series glycosphingolipids in pig organs indicates that iGb3 is unlikely to be a relevant immune epitope in xenotransplantation.
Figures




References
-
- Miyagawa S, Ueno T, Nagashima H, Takama Y, Fukuzawa M. Carbohydrate antigens. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2012;17(2):174–179. - PubMed
-
- Collins BH, Cotterell AH, McCurry KR, Alvarado CG, Magee JC, Parker W, Platt JL. Cardiac xenografts between primate species provide evidence for the importance of the alpha-galactosyl determinant in hyperacute rejection. J. Immunol. 1995;154(10):5500–5510. - PubMed
-
- Lin SS, Hanaway MJ, Gonzalez-Stawinski GV, Lau CL, Parker W, Davis RD, Byrne GW, Diamond LE, Logan JS, Platt JL. The role of anti-Galalpha1-3Gal antibodies in acute vascular rejection and accommodation of xenografts. Transplantation. 2000;70(12):1667–1674. - PubMed
-
- Xu H, Yin D, Naziruddin B, Chen L, Stark A, Wei Y, Lei Y, Shen J, Logan JS, Byrne GW, Chong AS. The in vitro and in vivo effects of anti-galactose antibodies on endothelial cell activation and xenograft rejection. J. Immunol. 2003;170(3):1531–1539. - PubMed
-
- Hauzenberger E, Klominek J, Holgersson J. Anti-Gal IgG potentiates natural killer cell migration across porcine endothelium via endothelial cell activation and increased natural killer cell motility triggered by CD16 cross-linking. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004;34(4):1154–1163. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
