Influence of cyclodextrin on the solubility and the polymerization of (meth)acrylated Triton(®) X-100
- PMID: 23378858
- PMCID: PMC3555431
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.8.245
Influence of cyclodextrin on the solubility and the polymerization of (meth)acrylated Triton(®) X-100
Abstract
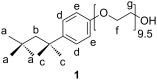
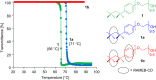
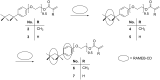
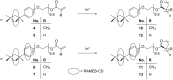
Triton(®) X-100 (poly(ethylene glycol) tert-octylphenyl ether) was (meth)acrylated and polymerized in the absence and presence of randomly methylated β-cyclodextrin (RAMEB-CD). Triton(®)-polymers that were polymerized with RAMEB-CD in water were compared with polymers that were synthesized in organic solvents after the addition of RAMEB-CD. The polymers were characterized by (1)H NMR and FTIR spectroscopy, matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS), dynamic light scattering (DLS), gel-permeation chromatography (GPC) and turbidity measurements. Additionally, the viscosity change of the methacrylic homopolymer with RAMEB-CD was evaluated.
Keywords: (meth)acrylated Triton®; Triton® X-100 (poly(ethylene glycol)tert-octylphenyl ether); randomly methylated β-cyclodextrin (RAMEB-CD); rheology.
Figures
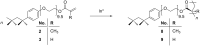
References
-
- Lindman B. Amphiphilic block copolymers: self-assembly and applications. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science; 2000.
-
- Larraz E, Elvira C, San Román J. J Polym Sci, Part A: Polym Chem. 2003;41:1641–1649. doi: 10.1002/pola.10710. - DOI
-
- Du X, Lu W, Ding N, Dai H, Teng X, Deng H. J Photochem Photobiol, A: Chem. 2006;177:76–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2005.05.014. - DOI
-
- Smith V K, Ndou T T, Muñoz De La Peña A, Warner I M. J Inclusion Phenom Macrocyclic Chem. 1991;10:471–484. doi: 10.1007/BF01061077. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
