The α-helical regions of KERP1 are important in Entamoeba histolytica adherence to human cells
- PMID: 23378906
- PMCID: PMC3558696
- DOI: 10.1038/srep01171
The α-helical regions of KERP1 are important in Entamoeba histolytica adherence to human cells
Abstract
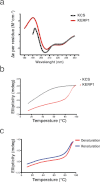
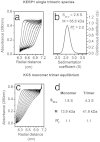
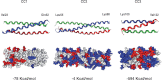
The lysine and glutamic acid rich protein KERP1 is a unique surface adhesion factor associated with virulence in the human pathogen Entamoeba histolytica. Both the function and structure of this protein remain unknown to this date. Here, we used circular dichroism, analytical ultracentrifugation and bioinformatics modeling to characterize the structure of KERP1. Our findings revealed that it is an α-helical rich protein organized as a trimer, endowed with a very high thermal stability (Tm = 89.6°C). Bioinformatics sequence analyses and 3D-structural modeling indicates that KERP1 central segments could account for protein trimerization. Relevantly, expressing the central region of KERP1 in living parasites, impair their capacity to adhere to human cells. Our observations suggest a link between the inhibitory effect of the isolated central region and the structural features of KERP1.
Figures
References
-
- Stanley S. L. Jr Amoebiasis. Lancet 361, 1025–1034 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Seigneur M., Mounier J., Prevost M. C. & Guillen N. A lysine- and glutamic acid-rich protein, KERP1, from Entamoeba histolytica binds to human enterocytes. Cell Microbiol 7, 569–579 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Santi-Rocca J. et al. The lysine- and glutamic acid-rich protein KERP1 plays a role in Entamoeba histolytica liver abscess pathogenesis. Cell Microbiol 10, 202–217 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Burkhard P., Stetefeld J. & Strelkov S. V. Coiled coils: a highly versatile protein folding motif. Trends Cell Biol 11, 82–88 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Parry D. A., Fraser R. D. & Squire J. M. Fifty years of coiled-coils and alpha-helical bundles: a close relationship between sequence and structure. J Struct Biol 163, 258–269 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

