Epidemiology of foodborne disease outbreaks caused by Clostridium perfringens, United States, 1998-2010
- PMID: 23379281
- PMCID: PMC4595929
- DOI: 10.1089/fpd.2012.1316
Epidemiology of foodborne disease outbreaks caused by Clostridium perfringens, United States, 1998-2010
Abstract
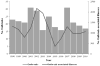
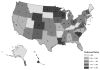
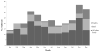
Clostridium perfringens is estimated to be the second most common bacterial cause of foodborne illness in the United States, causing one million illnesses each year. Local, state, and territorial health departments voluntarily report C. perfringens outbreaks to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention through the Foodborne Disease Outbreak Surveillance System. Our analysis included outbreaks confirmed by laboratory evidence during 1998-2010. A food item was implicated if C. perfringens was isolated from food or based on epidemiologic evidence. Implicated foods were classified into one of 17 standard food commodities when possible. From 1998 to 2010, 289 confirmed outbreaks of C. perfringens illness were reported with 15,208 illnesses, 83 hospitalizations, and eight deaths. The number of outbreaks reported each year ranged from 16 to 31 with no apparent trend over time. The annual number of outbreak-associated illnesses ranged from 359 to 2,173, and the median outbreak size was 24 illnesses. Outbreaks occurred year round, with the largest number in November and December. Restaurants (43%) were the most common setting of food preparation. Other settings included catering facility (19%), private home (16%), prison or jail (11%), and other (10%). Among the 144 (50%) outbreaks attributed to a single food commodity, beef was the most common commodity (66 outbreaks, 46%), followed by poultry (43 outbreaks, 30%), and pork (23 outbreaks, 16%). Meat and poultry outbreaks accounted for 92% of outbreaks with an identified single food commodity. Outbreaks caused by C. perfringens occur regularly, are often large, and can cause substantial morbidity yet are preventable if contamination of raw meat and poultry products is prevented at the farm or slaughterhouse or, after contamination, if these products are properly handled and prepared, particularly in restaurants and catering facilities.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Akhtar S, Paredes-Sabja D, Torres JA, Sarker MR. Strategy to inactivate Clostridium perfringens spores in meat products. Food Microbiol. 2009;26:272–277. - PubMed
-
- Bryan FL. What the sanitarian should know about Clostridium perfringens foodborne illness. J Milk Food Technol. 1969;32:381–389.
-
- Bryan FL, McKinley TW. Hazard analysis and control of roast beef preparation in foodservice establishments. J Food Prot. 1979;42:4–18. - PubMed
-
- Brynestad S, Granum PE. Clostridium perfringens and foodborne infections. Int J Food Microbiol. 2002;74:195–202. - PubMed
-
- [CDC] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Surveillance for foodborne disease outbreaks—United States, 1993–1997. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2000;49:1–62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

