Targeting calpain in synaptic plasticity
- PMID: 23379852
- PMCID: PMC4154356
- DOI: 10.1517/14728222.2013.766169
Targeting calpain in synaptic plasticity
Abstract
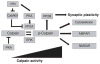
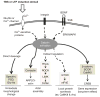
Introduction: Calpains represent a family of neutral, calcium-dependent proteases, which modify the function of their target proteins by partial truncation. These proteases have been implicated in numerous cell functions, including cell division, proliferation, migration, and death. In the CNS, where µ-calpain and m-calpain are the main calpain isoforms, their activation has been linked to synaptic plasticity as well as to neurodegeneration. This review will focus on the role of calpains in synaptic plasticity and discuss the possibility of developing methods to manipulate calpain activity for therapeutic purposes.
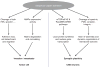
Areas covered: This review covers the literature showing how calpains are implicated in synaptic plasticity and in a number of conditions associated with learning impairment. The possibility of developing new drugs targeting these enzymes for treating these conditions is discussed.
Expert opinion: As evidence accumulates that calpain activation participates in neurodegeneration and cancer, there is interest in developing therapeutic approaches using direct or indirect calpain inhibition. In particular, a peptide derived from the calpain truncation site of mGluR1α was shown to decrease neurodegeneration following neonatal hypoxia/ischemia. More selective approaches need to be developed to target calpain or some of its substrates for therapeutic indications associated with deregulation of synaptic plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no other conflict of interest.
Figures
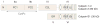
References
-
- Lynch G, Baudry M. The biochemistry of memory: a new and specific hypothesis. Science. 1984;224:1057–63. This was the first publication proposing a critical role for calpain in learning and memory. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Liu MC, Wang KK. Physiological and pathological actions of calpains in glutamatergic neurons. Sci Signal. 2008;1:tr3. Interesting review of the roles of calpains in plasticity and neurodegeneration. - PubMed
-
- Wu HY, Lynch DR. Calpain and synaptic function. Mol Neurobiol. 2006;33:215–36. Interesting review of the roles of calpains in plasticity and neurodegeneration. - PubMed
-
- Denny JB, Polan-Curtain J, Ghuman A, et al. Calpain inhibitors block long-term potentiation. Brain Res. 1990;534:317–20. - PubMed
-
- del Cerro S, Larson J, Oliver MW, et al. Development of hippocampal long-term potentiation is reduced by recently introduced calpain inhibitors. Brain Res. 1990;530:91–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
