De-SUMOylation enzyme of sentrin/SUMO-specific protease 2 regulates disturbed flow-induced SUMOylation of ERK5 and p53 that leads to endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis
- PMID: 23381569
- PMCID: PMC3697009
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.300179
De-SUMOylation enzyme of sentrin/SUMO-specific protease 2 regulates disturbed flow-induced SUMOylation of ERK5 and p53 that leads to endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis
Abstract
Rationale: Disturbed flow induces proinflammatory and apoptotic responses in endothelial cells, causing them to become dysfunctional and subsequently proatherogenic.
Objective: Although a possible link between SUMOylation of p53 and ERK5 detected during endothelial apoptosis and inflammation has been suggested, the mechanistic insights, especially under the proatherogenic flow condition, remain largely unknown.
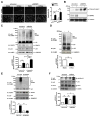
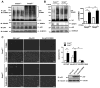
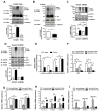
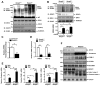
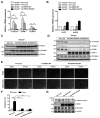
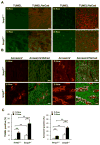
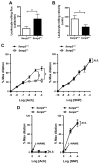
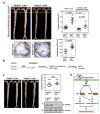
Methods and results: SUMOylation of p53 and ERK5 was induced by disturbed flow but not by steady laminar flow. To examine the role of the disturbed flow-induced p53 and ERK5 SUMOylation, we used de-SUMOylation enzyme of sentrin/Small Ubiquitin-like MOdifier (SUMO)-specific protease 2 deficiency (Senp2(+/-)) mice and observed a significant increase in endothelial apoptosis and adhesion molecule expression both in vitro and in vivo. These increases, however, were significantly inhibited in endothelial cells overexpressing p53 and ERK5 SUMOylation site mutants. Senp2(+/-) mice exhibited increased leukocyte rolling along the endothelium, and accelerated formation of atherosclerotic lesions was observed in Senp2(+/-)/Ldlr(-/-), but not in Senp2(+/+)/Ldlr(-/-), mice fed a high-cholesterol diet. Notably, the extent of lesion size in the aortic arch of Senp2(+/-)/Ldlr(-/-) mice was much larger than that in the descending aorta, also suggesting a crucial role of the disturbed flow-induced SUMOylation of proteins, including p53 and ERK5 in atherosclerosis formation.
Conclusions: These data show the unique role of sentrin/SUMO-specific protease 2 on endothelial function under disturbed flow and suggest that SUMOylation of p53 and ERK5 by disturbed flow contributes to the atherosclerotic plaque formation. Molecules involved in this newly discovered signaling will be useful targets for controlling endothelial cells dysfunction and consequently atherosclerosis formation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Disturbed flow-activated p90RSK kinase accelerates atherosclerosis by inhibiting SENP2 function.J Clin Invest. 2015 Mar 2;125(3):1299-310. doi: 10.1172/JCI76453. Epub 2015 Feb 17. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 25689261 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 SUMOylation antagonizes shear stress-induced antiinflammatory response and endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression in endothelial cells.Circ Res. 2008 Mar 14;102(5):538-45. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.156877. Epub 2008 Jan 24. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18218985
-
Phosphorylation of protein inhibitor of activated STAT1 (PIAS1) by MAPK-activated protein kinase-2 inhibits endothelial inflammation via increasing both PIAS1 transrepression and SUMO E3 ligase activity.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Feb;33(2):321-9. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300619. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23202365 Free PMC article.
-
Disturbed Flow-Induced Endothelial Proatherogenic Signaling Via Regulating Post-Translational Modifications and Epigenetic Events.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016 Sep 1;25(7):435-50. doi: 10.1089/ars.2015.6556. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016. PMID: 26714841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disturbed-flow-mediated vascular reactive oxygen species induce endothelial dysfunction.Circ J. 2011;75(12):2722-30. doi: 10.1253/circj.cj-11-1124. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Circ J. 2011. PMID: 22076424 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Disturbed flow-activated p90RSK kinase accelerates atherosclerosis by inhibiting SENP2 function.J Clin Invest. 2015 Mar 2;125(3):1299-310. doi: 10.1172/JCI76453. Epub 2015 Feb 17. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 25689261 Free PMC article.
-
Flow signaling and atherosclerosis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 May;74(10):1835-1858. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2442-4. Epub 2016 Dec 30. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28039525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative analysis of the expression profile and prognostic values of SENP gene family in hepatocellular carcinoma.Discov Oncol. 2025 May 13;16(1):752. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02598-w. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40358846 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia Triggers SENP1 (Sentrin-Specific Protease 1) Modulation of KLF15 (Kruppel-Like Factor 15) and Transcriptional Regulation of Arg2 (Arginase 2) in Pulmonary Endothelium.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Apr;38(4):913-926. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.310660. Epub 2018 Feb 22. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29472234 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation targeting mitophagy in cardiovascular diseases.J Mol Med (Berl). 2022 Nov;100(11):1511-1538. doi: 10.1007/s00109-022-02258-4. Epub 2022 Sep 26. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022. PMID: 36163375 Review.
References
-
- Libby P, Ridker PM, Maseri A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2002;105:1135–1143. - PubMed
-
- Berk BC. Atheroprotective signaling mechanisms activated by steady laminar flow in endothelial cells. Circulation. 2008;117:1082–1089. - PubMed
-
- Malek AM, Alper SL, Izumo S. Hemodynamic shear stress and its role in atherosclerosis. JAMA : the journal of the American Medical Association. 1999;282:2035–2042. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

