Separation and purification of multiply acetylated proteins using cation-exchange chromatography
- PMID: 23381856
- PMCID: PMC3779653
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-62703-305-3_8
Separation and purification of multiply acetylated proteins using cation-exchange chromatography
Abstract
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is extremely useful for the study of proteins and the characterization of their posttranslational modifications. Here we describe a method that utilizes cation-exchange HPLC to separate multiply acetylated histone H3 species on the basis of their charge and hydrophilicity. This high-resolution method allows for the separation of histone H3 species that differ by as few as one acetyl group, and is compatible with subsequent analysis by a variety of techniques, including mass spectrometry and western blotting.
Figures
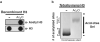


References
-
- Garcia BA, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF. Characterization of histones and their post-translational modifications by mass spectrometry. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2007;11:66–73. - PubMed
-
- Thomas CE, Kelleher NL, Mizzen CA. Mass spectrometric characterization of human H3: a bird's eye view. J Prot Res. 2006;5:240–247. - PubMed
-
- Lindner HH. Analysis of histones, histone variants, and their post-translationally modified forms. Electrophoresis. 2008;29:2516–2532. - PubMed
-
- Zhang K, Siino JS, Jones PR, Yau PM, Bradbury EM. A mass spectrometric “Western blot” to evaluate the correlations between histone methylation and histone acetylation. Proteomics. 2004;4:3765–3775. - PubMed
-
- Alpert AJ. Cation-exchange high-performance liquid chromatography of proteins on poly(aspartic acid)-silica. J Chromatogr. 1983;266:23–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

