Proteomic analysis of ubiquitin ligase KEAP1 reveals associated proteins that inhibit NRF2 ubiquitination
- PMID: 23382044
- PMCID: PMC3618590
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4400
Proteomic analysis of ubiquitin ligase KEAP1 reveals associated proteins that inhibit NRF2 ubiquitination
Abstract
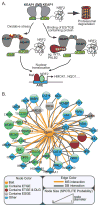
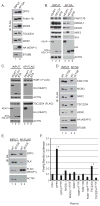
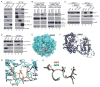
Somatic mutations in the KEAP1 ubiquitin ligase or its substrate NRF2 (NFE2L2) commonly occur in human cancer, resulting in constitutive NRF2-mediated transcription of cytoprotective genes. However, many tumors display high NRF2 activity in the absence of mutation, supporting the hypothesis that alternative mechanisms of pathway activation exist. Previously, we and others discovered that via a competitive binding mechanism, the proteins WTX (AMER1), PALB2, and SQSTM1 bind KEAP1 to activate NRF2. Proteomic analysis of the KEAP1 protein interaction network revealed a significant enrichment of associated proteins containing an ETGE amino acid motif, which matches the KEAP1 interaction motif found in NRF2. Like WTX, PALB2, and SQSTM1, we found that the dipeptidyl peptidase 3 (DPP3) protein binds KEAP1 via an "ETGE" motif to displace NRF2, thus inhibiting NRF2 ubiquitination and driving NRF2-dependent transcription. Comparing the spectrum of KEAP1-interacting proteins with the genomic profile of 178 squamous cell lung carcinomas characterized by The Cancer Genome Atlas revealed amplification and mRNA overexpression of the DPP3 gene in tumors with high NRF2 activity but lacking NRF2 stabilizing mutations. We further show that tumor-derived mutations in KEAP1 are hypomorphic with respect to NRF2 inhibition and that DPP3 overexpression in the presence of these mutants further promotes NRF2 activation. Collectively, our findings further support the competition model of NRF2 activation and suggest that "ETGE"-containing proteins such as DPP3 contribute to NRF2 activity in cancer.
©2013 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Kensler TW, Wakabayashi N, Biswal S. Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;47:89–116. - PubMed
-
- Singh A, Boldin-Adamsky S, Thimmulappa RK, Rath SK, Ashush H, Coulter J, et al. RNAi-mediated silencing of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 gene expression in non-small cell lung cancer inhibits tumor growth and increases efficacy of chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2008;68:7975–84. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ohta T, Iijima K, Miyamoto M, Nakahara I, Tanaka H, Ohtsuji M, et al. Loss of Keap1 function activates Nrf2 and provides advantages for lung cancer cell growth. Cancer Res. 2008;68:1303–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

