8-CPT-cAMP/all-trans retinoic acid targets t(11;17) acute promyelocytic leukemia through enhanced cell differentiation and PLZF/RARα degradation
- PMID: 23382200
- PMCID: PMC3587232
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1222863110
8-CPT-cAMP/all-trans retinoic acid targets t(11;17) acute promyelocytic leukemia through enhanced cell differentiation and PLZF/RARα degradation
Abstract
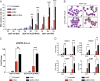
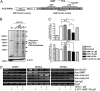
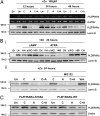
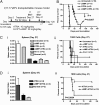
The refractoriness of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) with t(11;17)(q23;q21) to all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA)-based therapy concerns clinicians and intrigues basic researchers. By using a murine leukemic model carrying both promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger/retinoic acid receptor-α (PLZF/RARα) and RARα/PLZF fusion genes, we discovered that 8-chlorophenylthio adenosine-3', 5'-cyclic monophosphate (8-CPT-cAMP) enhances cellular differentiation and improves gene trans-activation by ATRA in leukemic blasts. Mechanistically, in combination with ATRA, 8-CPT-cAMP activates PKA, causing phosphorylation of PLZF/RARα at Ser765 and resulting in increased dissociation of the silencing mediator for retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors/nuclear receptor corepressor from PLZF/RARα. This process results in changes of local chromatin and transcriptional reactivation of the retinoic acid pathway in leukemic cells. Meanwhile, 8-CPT-cAMP also potentiated ATRA-induced degradation of PLZF/RARα through its Ser765 phosphorylation. In vivo treatment of the t(11;17) APL mouse model demonstrated that 8-CPT-cAMP could significantly improve the therapeutic effect of ATRA by targeting a leukemia-initiating cell activity. This combined therapy, which induces enhanced differentiation and oncoprotein degradation, may benefit t(11;17) APL patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zelent A, Guidez F, Melnick A, Waxman S, Licht JD. Translocations of the RARalpha gene in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Oncogene. 2001;20(49):7186–7203. - PubMed
-
- Wang ZY, Chen Z. Acute promyelocytic leukemia: From highly fatal to highly curable. Blood. 2008;111(5):2505–2515. - PubMed
-
- Licht JD, et al. Clinical and molecular characterization of a rare syndrome of acute promyelocytic leukemia associated with translocation (11;17) Blood. 1995;85(4):1083–1094. - PubMed
-
- Jansen JH, et al. Complete remission of t(11;17) positive acute promyelocytic leukemia induced by all-trans retinoic acid and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Blood. 1999;94(1):39–45. - PubMed
-
- Petti MC, et al. Complete remission through blast cell differentiation in PLZF/RARalpha-positive acute promyelocytic leukemia: in vitro and in vivo studies. Blood. 2002;100(3):1065–1067. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

