Essential requirement for IRF8 and SLC15A4 implicates plasmacytoid dendritic cells in the pathogenesis of lupus
- PMID: 23382217
- PMCID: PMC3581947
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1222798110
Essential requirement for IRF8 and SLC15A4 implicates plasmacytoid dendritic cells in the pathogenesis of lupus
Abstract
In vitro evidence suggests that plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) are intimately involved in the pathogenesis of lupus. However, it remains to be determined whether these cells are required in vivo for disease development, and whether their contribution is restricted to hyperproduction of type I IFNs. To address these issues, we created lupus-predisposed mice lacking the IFN regulatory factor 8 (IRF8) or carrying a mutation that impairs the peptide/histidine transporter solute carrier family 15, member 4 (SLC15A4). IRF8-deficient NZB mice, lacking pDCs, showed almost complete absence of anti-nuclear, anti-chromatin, and anti-erythrocyte autoantibodies, along with reduced kidney disease. These effects were observed despite normal B-cell responses to Toll-like receptor (TLR) 7 and TLR9 stimuli and intact humoral responses to conventional T-dependent and -independent antigens. Moreover, Slc15a4 mutant C57BL/6-Fas(lpr) mice, in which pDCs are present but unable to produce type I IFNs in response to endosomal TLR ligands, also showed an absence of autoantibodies, reduced lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly, and extended survival. Taken together, our results demonstrate that pDCs and the production of type I IFNs by these cells are critical contributors to the pathogenesis of lupus-like autoimmunity in these models. Thus, IRF8 and SLC15A4 may provide important targets for therapeutic intervention in human lupus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
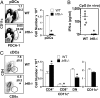
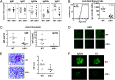


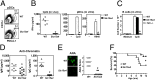

References
-
- Baechler EC, Gregersen PK, Behrens TW. The emerging role of interferon in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Immunol. 2004;16(6):801–807. - PubMed
-
- Kirou KA, et al. Activation of the interferon-alpha pathway identifies a subgroup of systemic lupus erythematosus patients with distinct serologic features and active disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(5):1491–1503. - PubMed
-
- Braun D, Geraldes P, Demengeot J. Type I interferon controls the onset and severity of autoimmune manifestations in lpr mice. J Autoimmun. 2003;20(1):15–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AR053228/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1U19-AI100627-01/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR039555/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI070167/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AR39555/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR53228/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR031203/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AR039555/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR065384/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR31203/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI100627/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 2P01-AI070167-06A1/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

